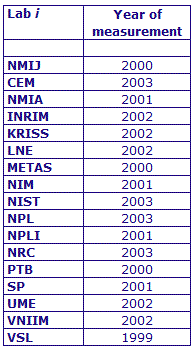
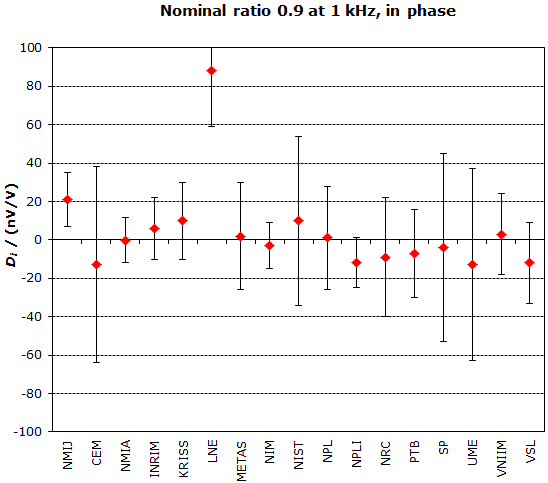
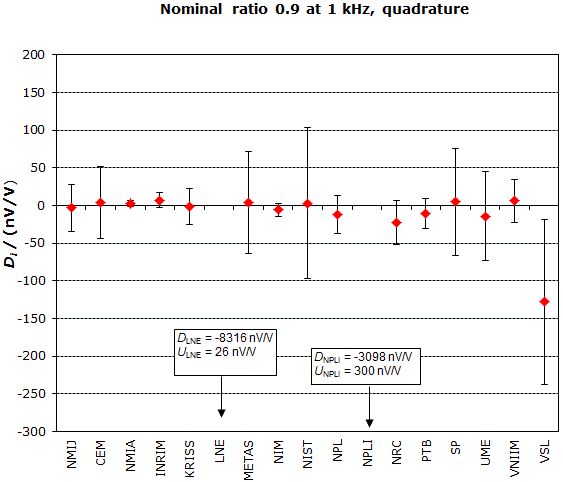
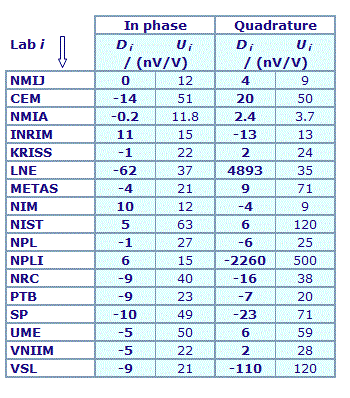
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.9
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
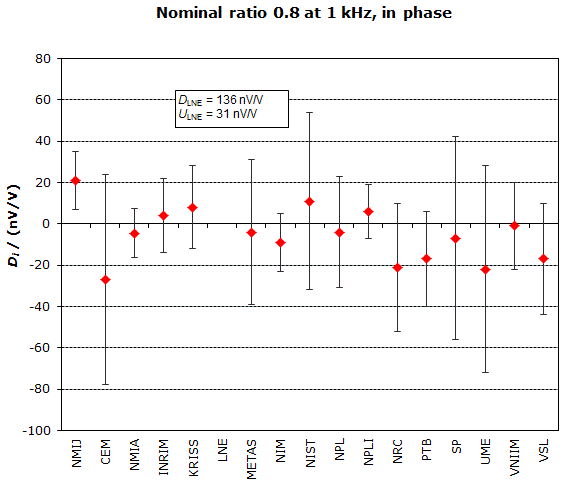
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.8
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
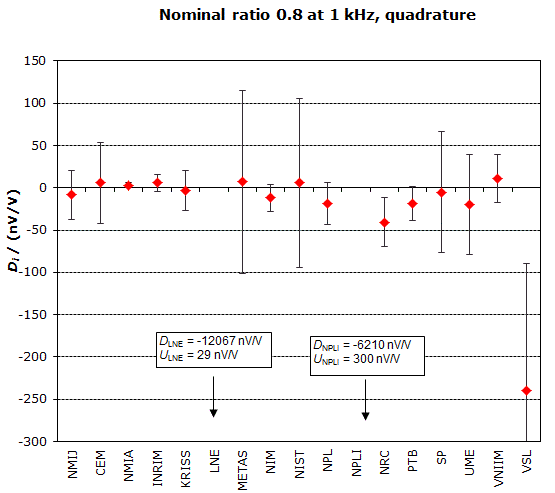
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.7
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
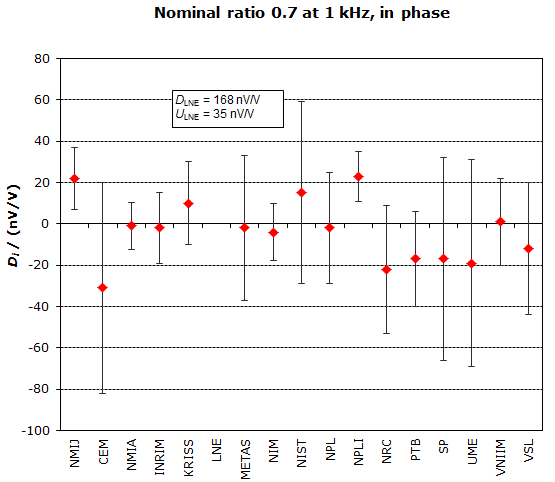
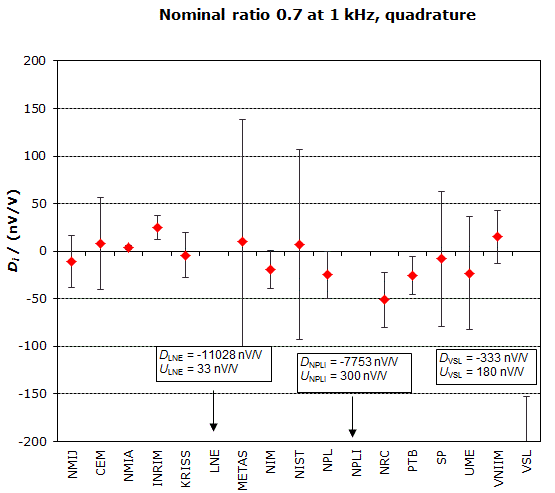
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.6
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
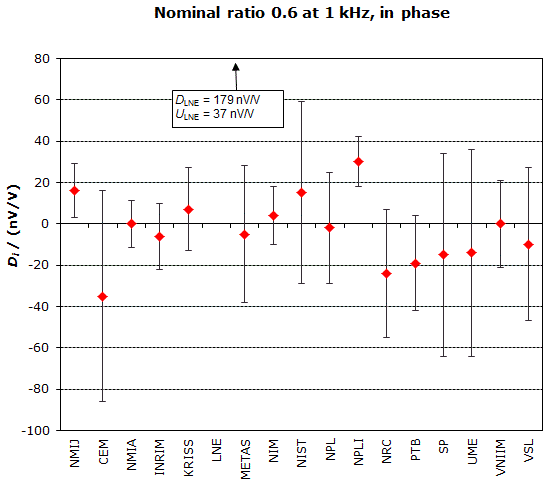
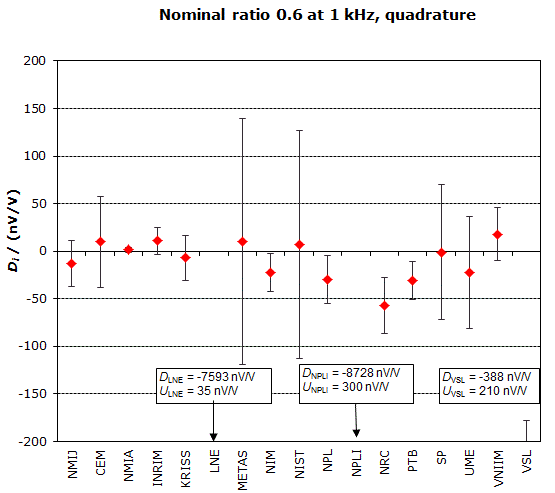
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.5
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
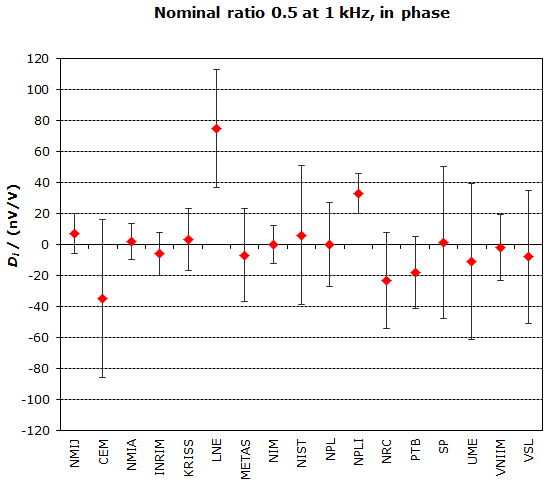
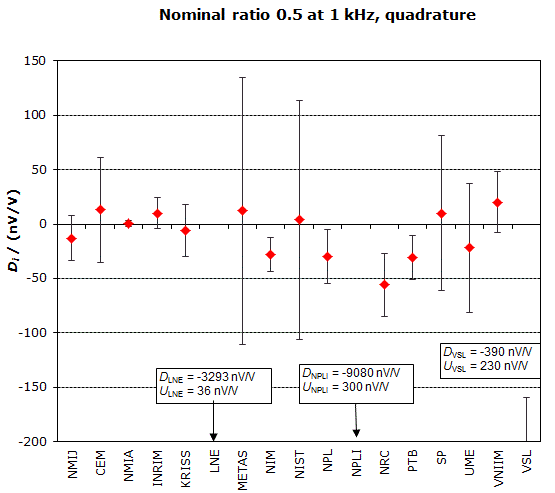
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
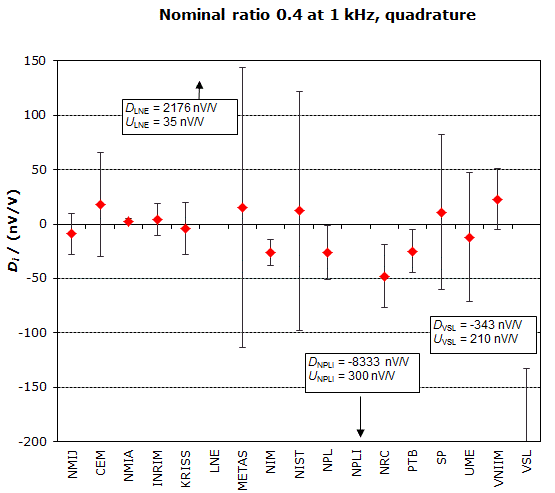
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.4
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
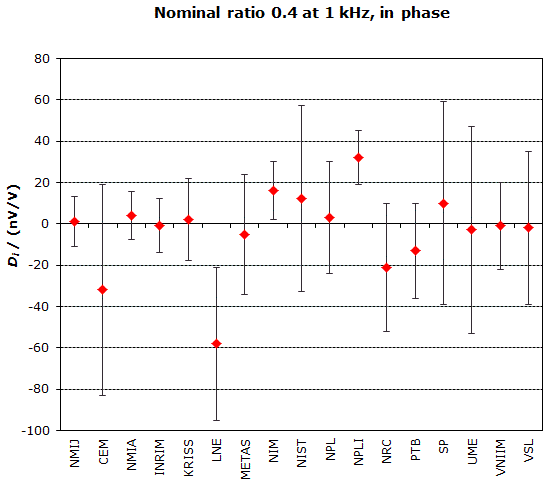
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
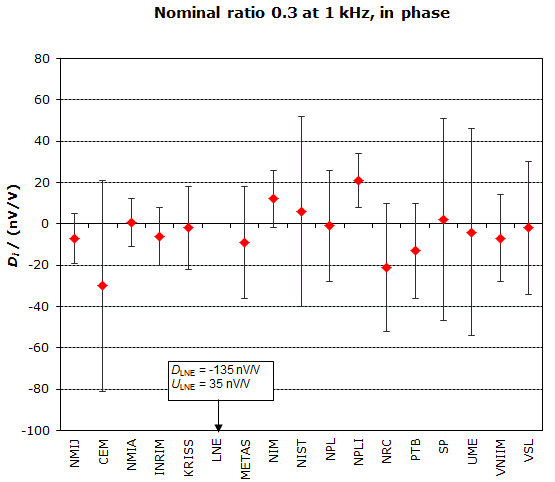
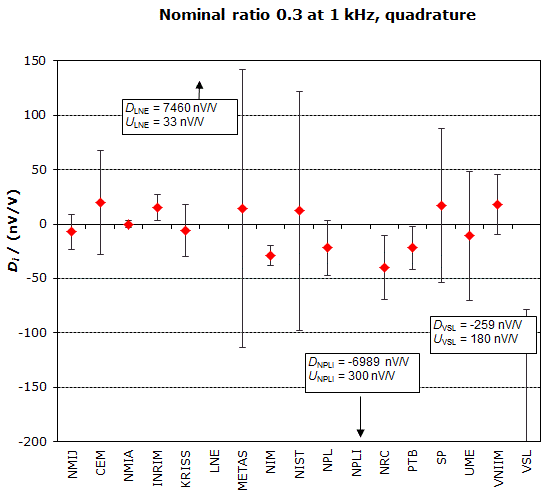
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.3
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
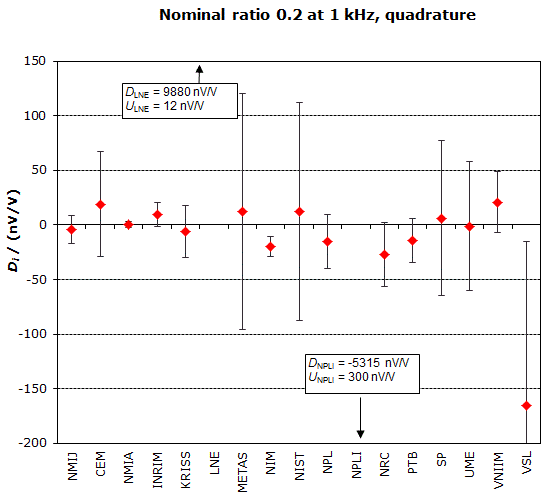
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
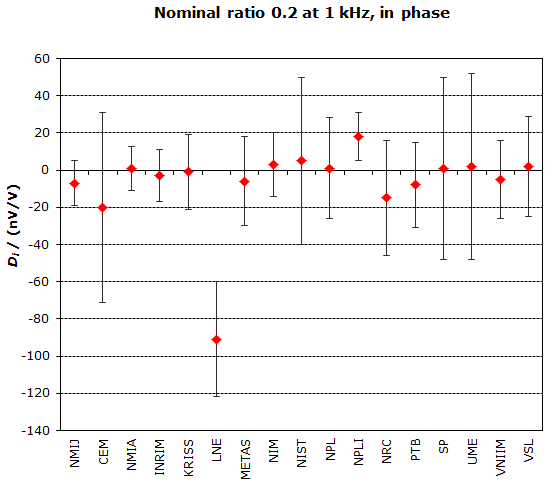
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.2
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
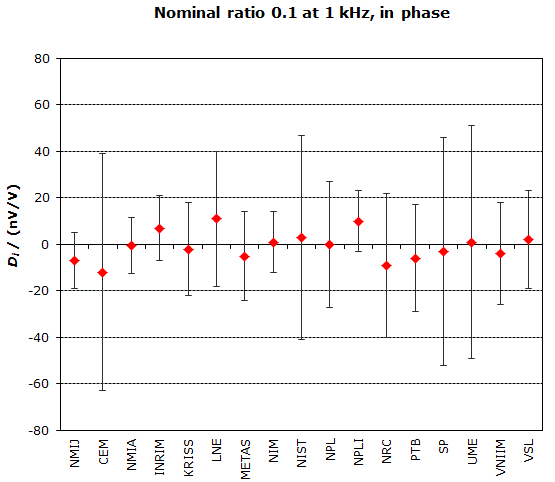
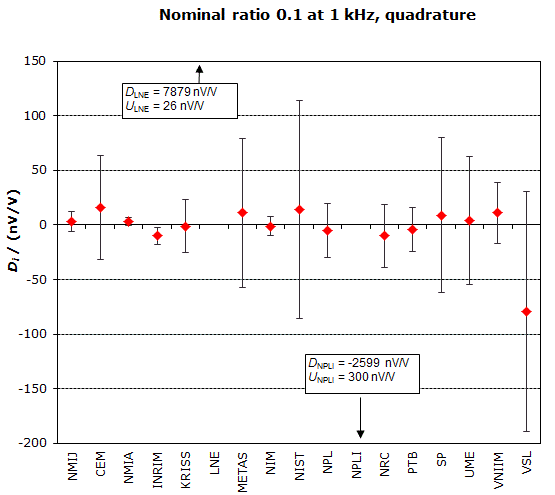
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.1
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
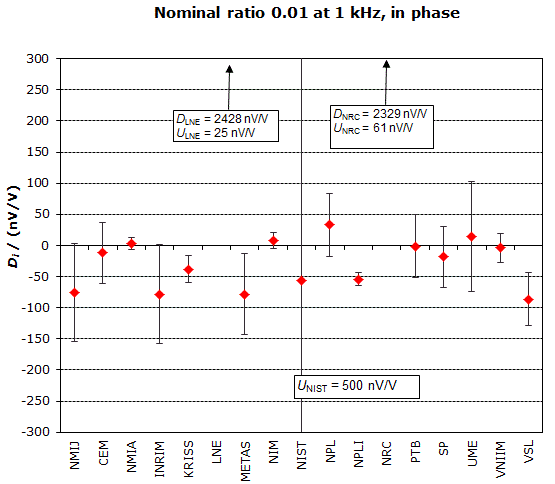
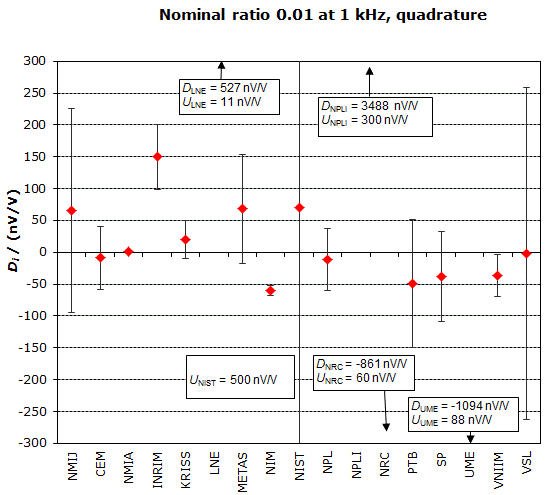
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.01
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
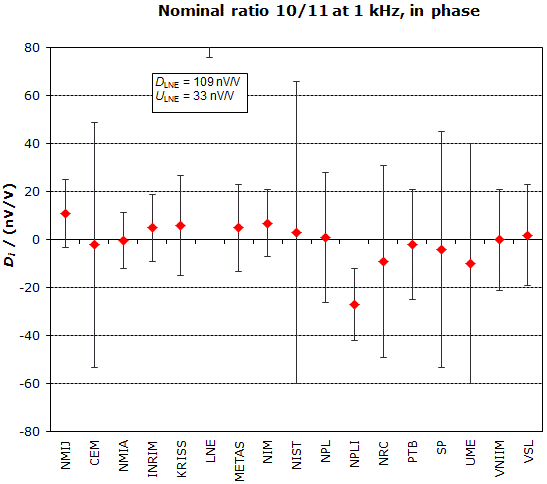
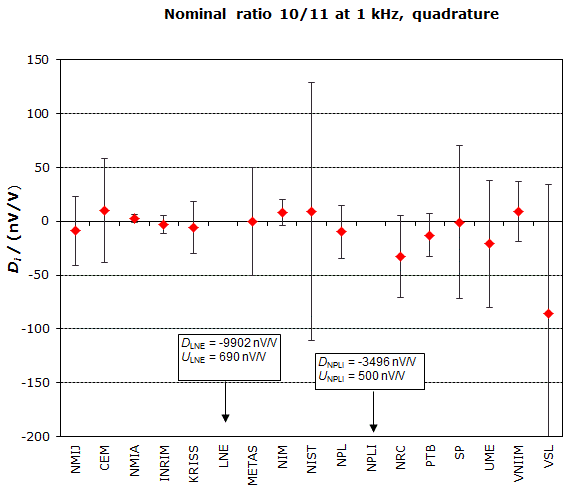
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 10/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
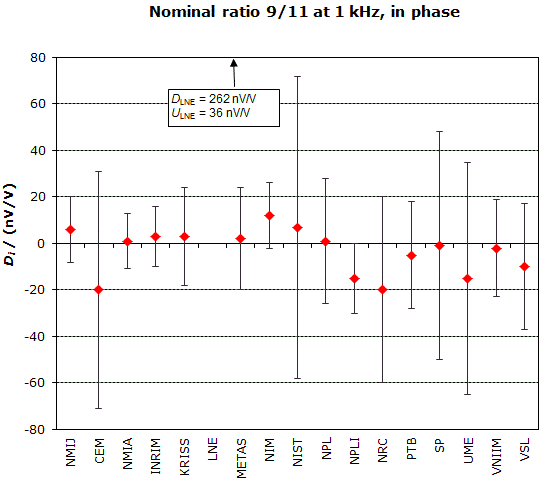
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 9/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
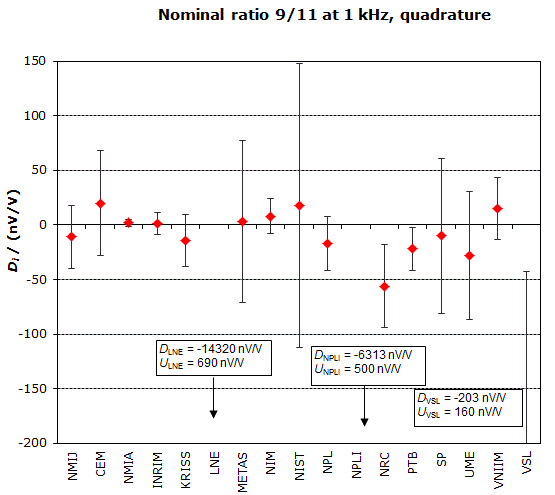
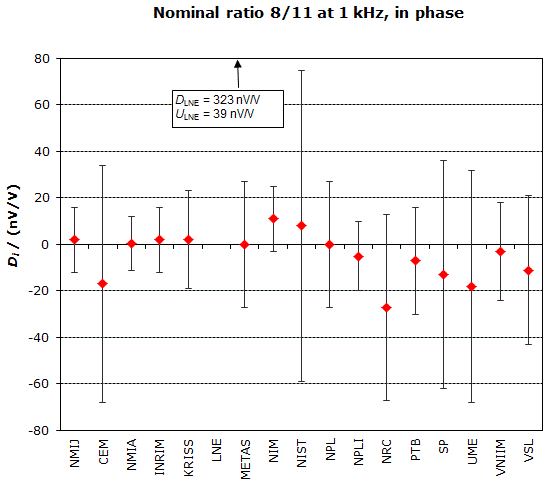
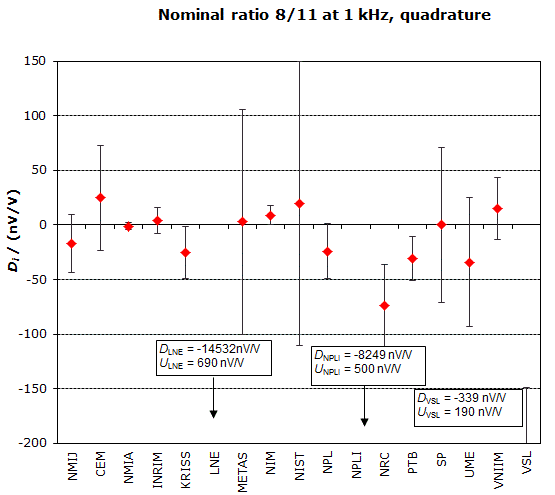
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 8/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 7/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
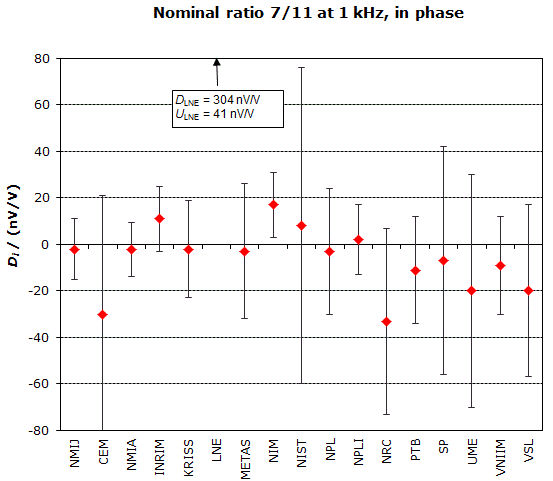
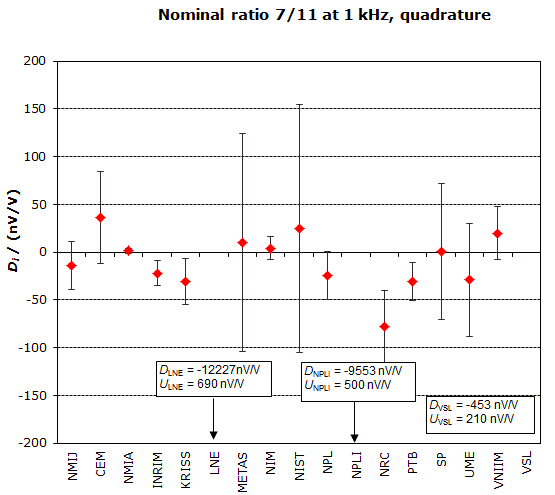
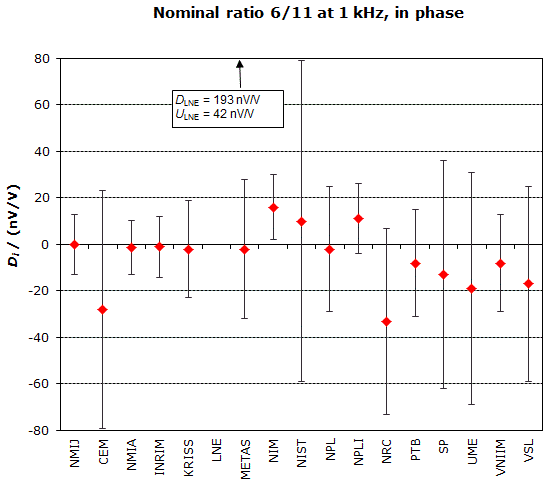
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 6/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
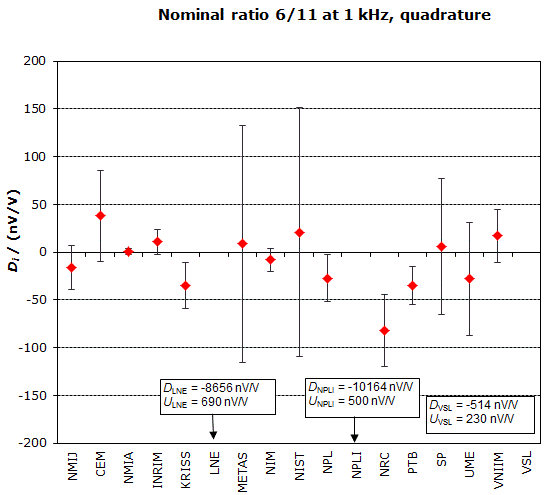
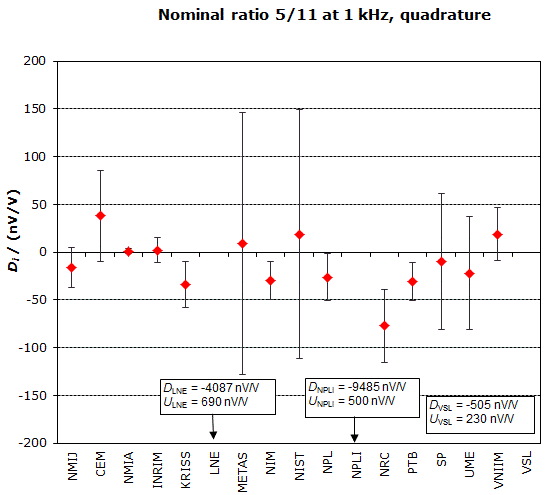
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 5/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
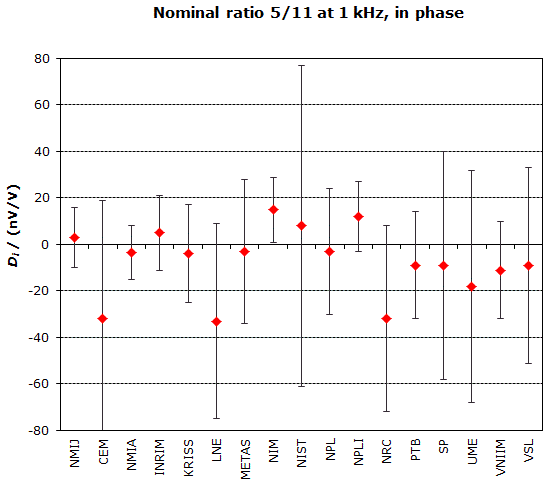
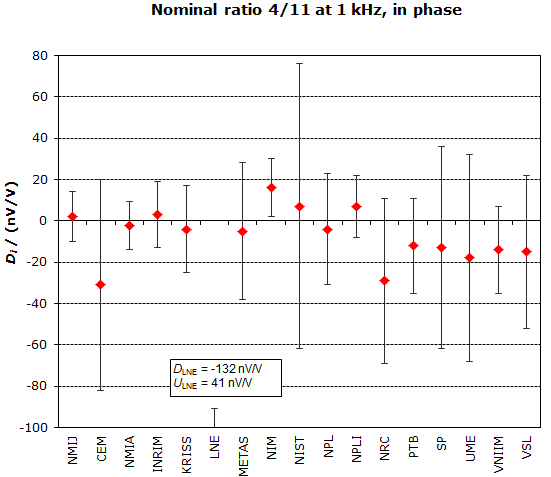
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 4/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
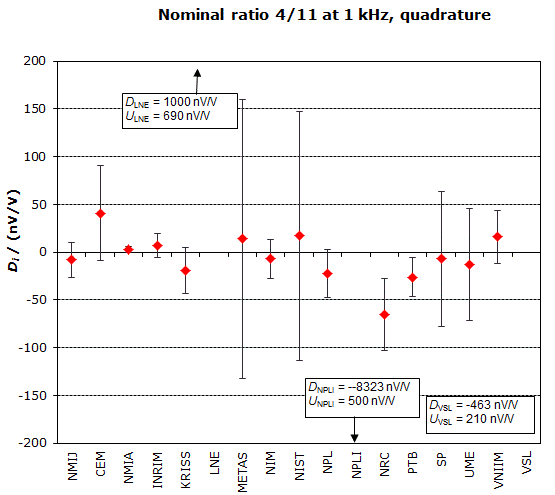
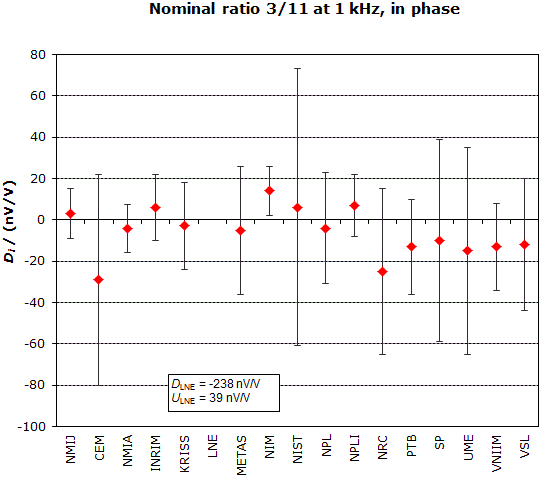
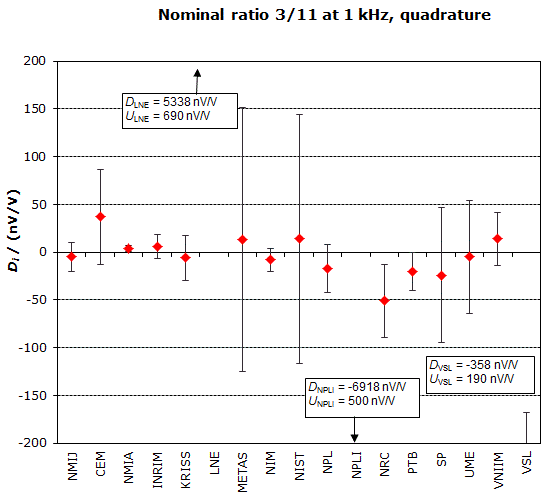
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 3/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
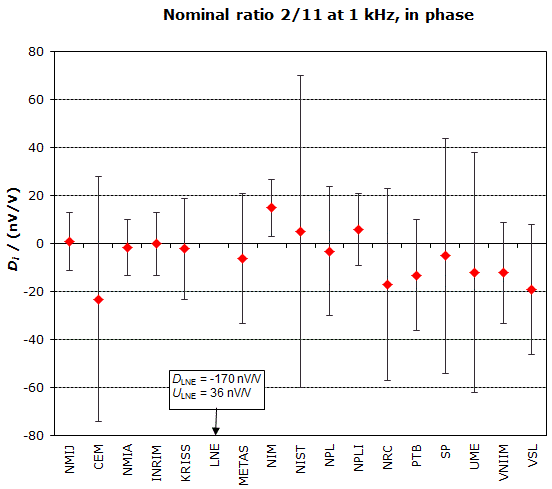
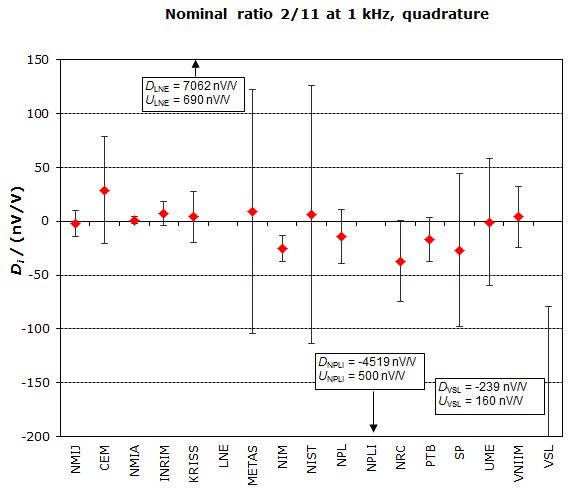
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 2/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
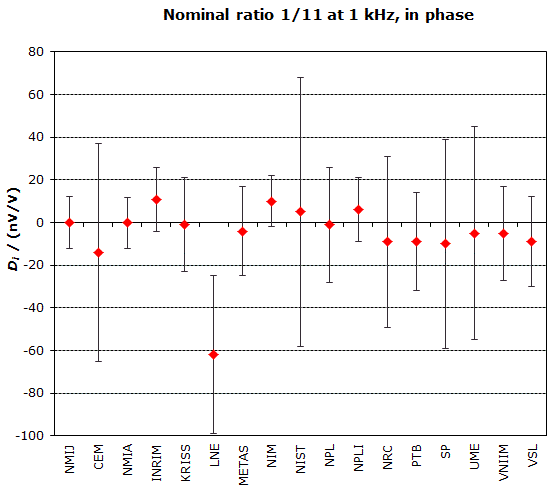
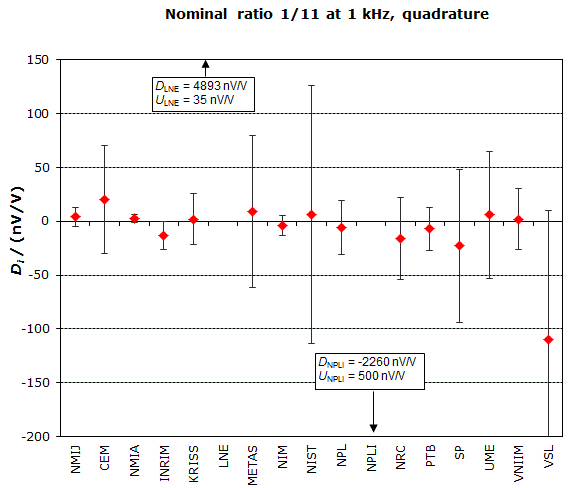
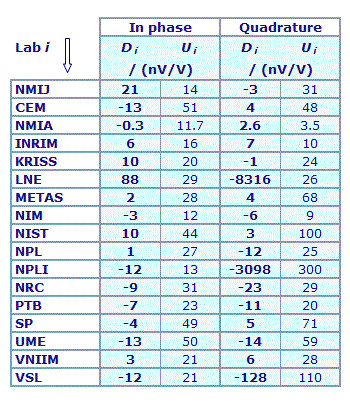
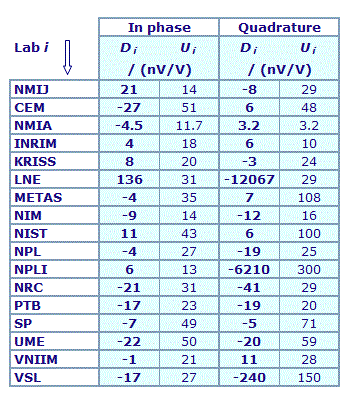
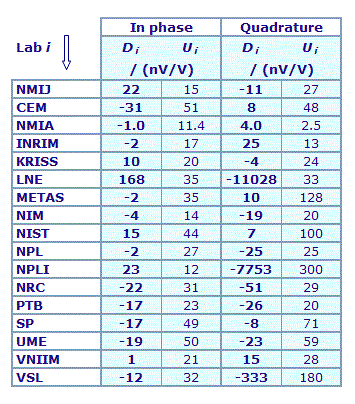
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 1/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V, for the in-phase and the quadrature components of the voltage ratio
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.9
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.8
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.7
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.6
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
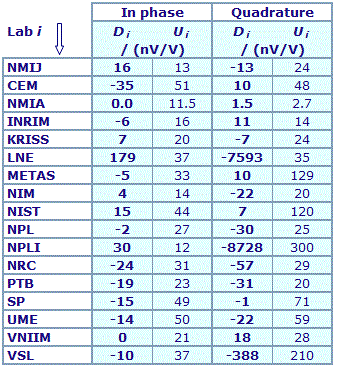
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.5
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
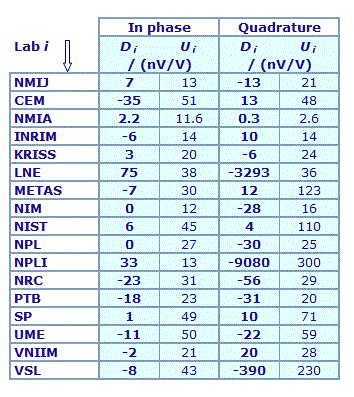
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.4
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
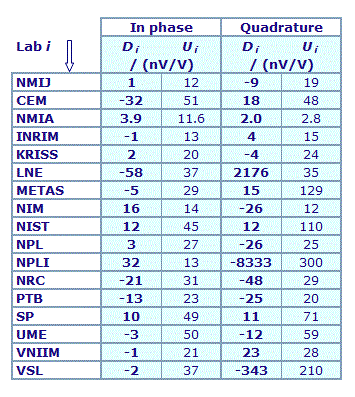
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.3
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
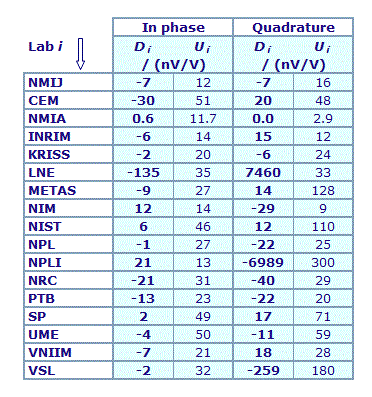
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.2
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
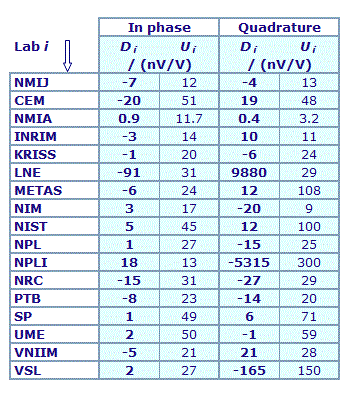
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.1
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
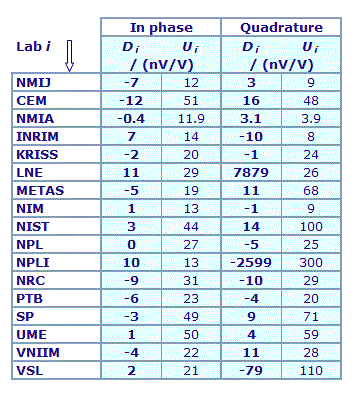
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.01
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
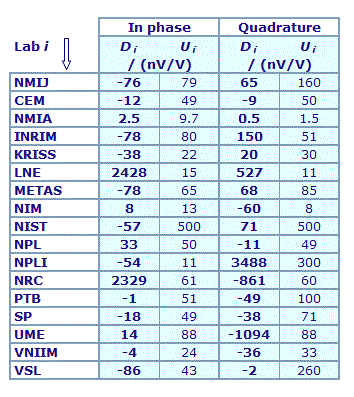
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 10/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
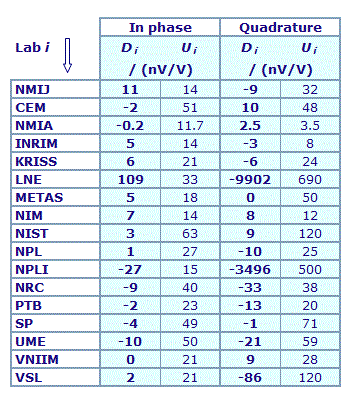
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 9/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
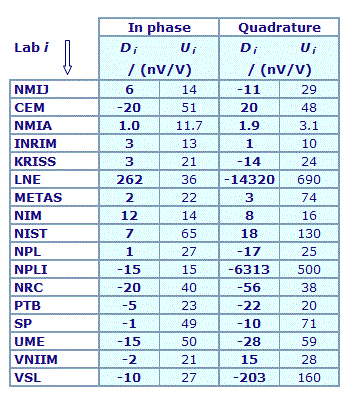
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 8/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
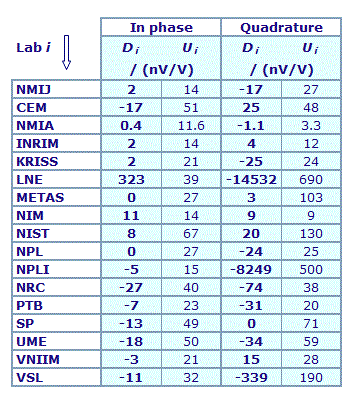
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 7/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
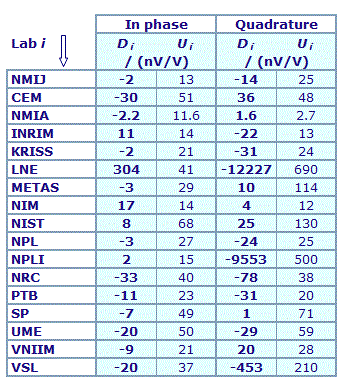
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 6/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
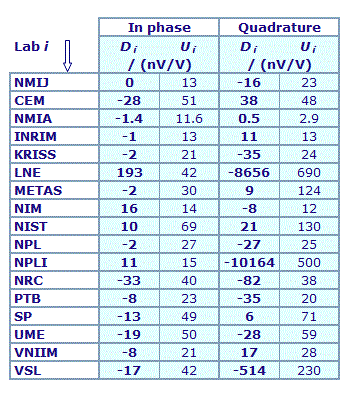
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 5/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
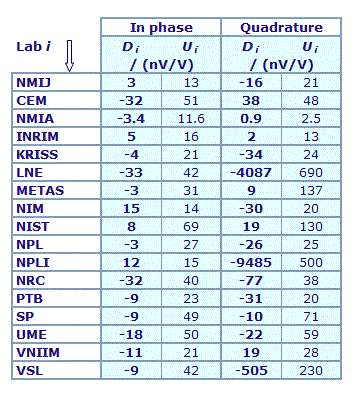
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 4/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
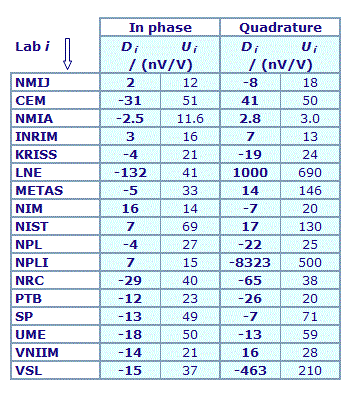
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 3/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
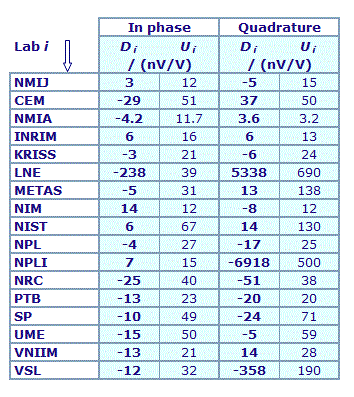
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 2/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
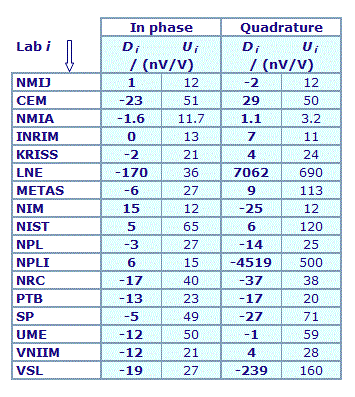
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 1/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
Degrees of equivalence: Di and expanded uncertainty Ui (k = 2),
both expressed in nV/V
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (PDF file).
| Metrology area, Sub-field | Electricity and Magnetism, AC Voltage, Current, Power, and AC/DC Transfer |
| Description | AC voltage ratio |
| Time of measurements | 1999 - 2003 |
| Status | Approved for equivalence |
| Final Reports of the comparisons | |
| Measurand | AC voltage ratio |
| Parameters | Frequency: 1 kHz and 55 Hz (optional) |
| Transfer device | Inductive voltage divider |
| Comparison type | Key Comparison |
| Consultative Committee | CCEM (Consultative Committee for Electricity and Magnetism) |
| Conducted by | CCEM (Consultative Committee for Electricity and Magnetism) |
| Comments | Results published on 10 June 2012 AC voltage ratio |
| Pilot institute |
NPL
National Physical Laboratory United Kingdom |
| Contact person | I. Robinson +44 (0) 20 8943 7139 |
| Pilot laboratory | |
|---|---|
| NPL |
National Physical Laboratory, United Kingdom, EURAMET |
| CEM |
Centro Español de Metrologia, Spain, EURAMET |
| INRIM |
Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica, Italy, EURAMET |
| KRISS |
Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Korea, Republic of, APMP |
| LNE |
Laboratoire national de métrologie et d'essais, France, EURAMET |
| METAS |
Federal Institute of Metrology, Switzerland, EURAMET |
| NIM |
National Institute of Metrology, China, APMP |
| NIST |
National Institute of Standards and Technology, United States, SIM |
| NMIA |
National Measurement Institute, Australia, Australia, APMP |
| NMIJ AIST |
National Metrology Institute of Japan, Japan, APMP |
| NPLI |
CSIR National Physical Laboratory of India, India, APMP |
| NRC |
National Research Council, Canada, SIM |
| PTB |
Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Germany, EURAMET |
| SP |
Technical Research Institute of Sweden from 2017 Research Institutes of Sweden AB, Sweden, EURAMET |
| UME |
TÜBITAK Ulusal Metroloji Enstitüsü, Türkiye, EURAMET |
| VNIIM |
D.I. Mendeleyev Institute for Metrology, Rosstandart, Russian Federation, COOMET |
| VSL |
VSL, Netherlands, EURAMET |
This page proposes print-out on A4 paper (portrait) of the comparison details (best printed out using a black and white printer).
Please, select items to be printed out, then click on "OK" :
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.9
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 58.3 nV/V and UR = 5.1 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -71.6 nV/V and UR = 3.9 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.8
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 71.5 nV/V and UR = 5.3 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -110.2 nV/V and UR = 4.1 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.7
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 64.0 nV/V and UR = 5.8 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -137.0 nV/V and UR = 4.5 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.6
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 39.0 nV/V and UR = 5.7 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -132.5 nV/V and UR = 4.4 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.5
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 9.8 nV/V and UR = 5.4 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -130.3 nV/V and UR = 4.5 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.4
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -22.9 nV/V and UR = 5.4 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -97.0 nV/V and UR = 4.4 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.3
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -38.6 nV/V and UR = 5.1 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -51.0 nV/V and UR = 4.3 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.2
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -45.9 nV/V and UR = 5.1 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -15.4 nV/V and UR = 4.1 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.1
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -43.6 nV/V and UR = 4.8 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = 8.9 nV/V and UR = 3.5 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.01
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -1160.5 nV/V and UR = 8.4 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = 422.5 nV/V and UR = 5.0 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 10/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 53.2 nV/V and UR = 5.1 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -123.5 nV/V and UR = 3.9 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 9/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 21.8 nV/V and UR = 5.2 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -176.9 nV/V and UR = 4.1 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 8/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = 9.4 nV/V and UR = 5.3 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -200.9 nV/V and UR = 4.0 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 7/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -6.2 nV/V and UR = 5.3 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -186.6 nV/V and UR = 4.5 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 6/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -17.1 nV/V and UR = 5.3 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -156.5 nV/V and UR = 4.3 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 5/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -2.2 nV/V and UR = 5.4 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -124.9 nV/V and UR = 4.6 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 4/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -31.1 nV/V and UR = 5.4 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -46.8 nV/V and UR = 4.3 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 3/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -24.5 nV/V and UR = 5.3 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = -1.6 nV/V and UR = 4.1 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 2/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -46.2 nV/V and UR = 5.1 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = 48.9 nV/V and UR = 4.1 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 1/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
| The key comparison reference value, xR, is calculated as the weighted mean of the participants' results with exclusion of outliers. Its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), UR, is calculated as explained in section 1.3 of the Final Report, Part 2. |
In phase : xR = -49.7 nV/V and UR = 5.0 nV/V
Quadrature : xR = 59.6 nV/V and UR = 3.7 nV/V
| The degree of equivalence of each laboratory with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di and Ui, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V. |
| The degree of equivalence between two laboratories i and j is given by a pair of terms: Dij and Uij, its expanded uncertainty (k = 2), both expressed in nV/V, and can be found in section 3 of the Final report, Part 2. |
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.9
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.8
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.7
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.6
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
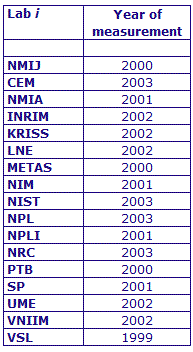
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.5
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
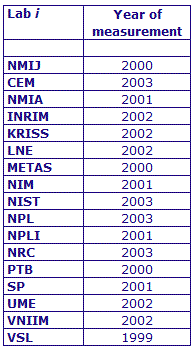
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.4
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
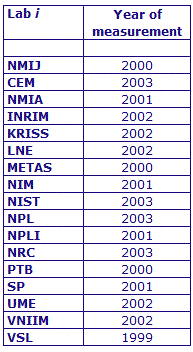
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.3
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
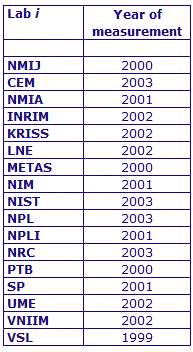
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.2
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
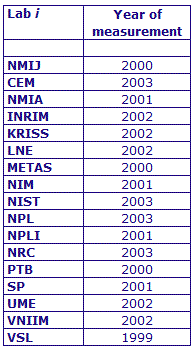
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.1
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
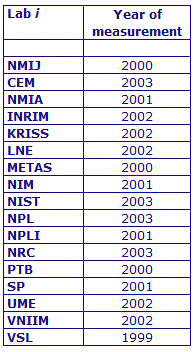
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 0.01
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
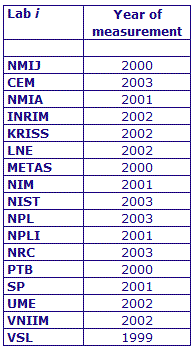
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 10/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
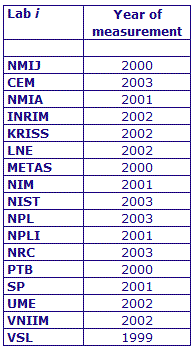
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 9/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
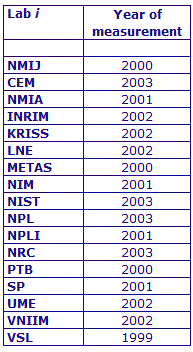
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 8/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
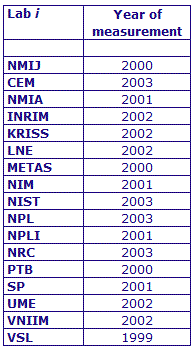
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 7/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
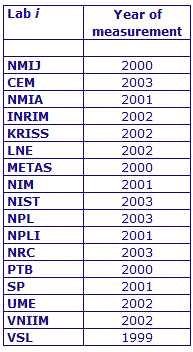
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 6/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
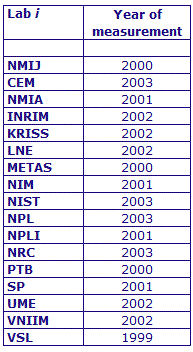
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 5/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
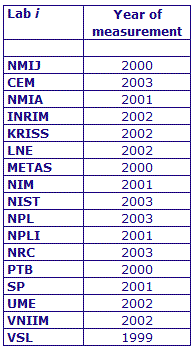
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 4/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
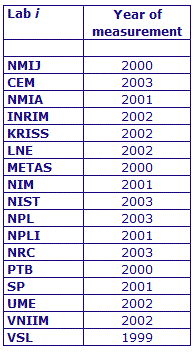
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 3/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
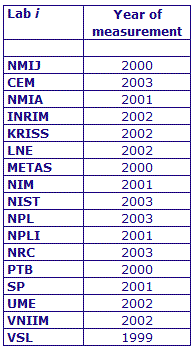
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 2/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.
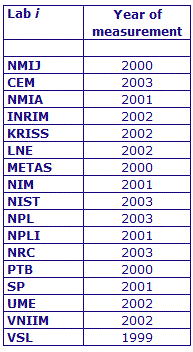
MEASURAND : AC Voltage ratio
NOMINAL RATIO VALUE : 1/11
FREQUENCY : 1 kHz
The measurements of this key comparison were made of twenty AC voltage ratios at two possible frequencies: 1 kHz and 55 Hz. The in-phase and quadrature components of each voltage ratio were reported separately giving a total of 80 possible measurement results for each participant. The 1 kHz measurements were compulsory and all the 17 participating laboratories made these measurements. The 55 Hz measurements were optional, with 7 laboratories contributing.
The measurement results reported by the laboratories participating in CCEM-K7 can be found in section 4 on page 188 of the Final Report, Part 2.