

CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 250 nm to 360 nm
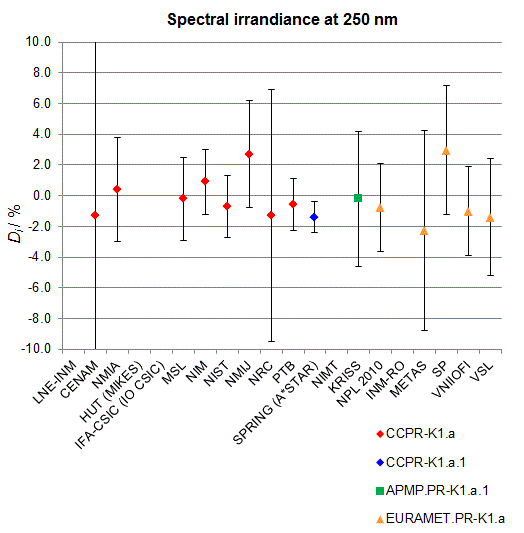
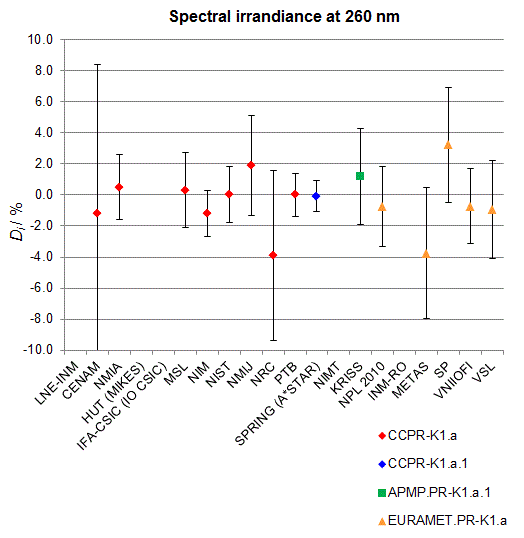
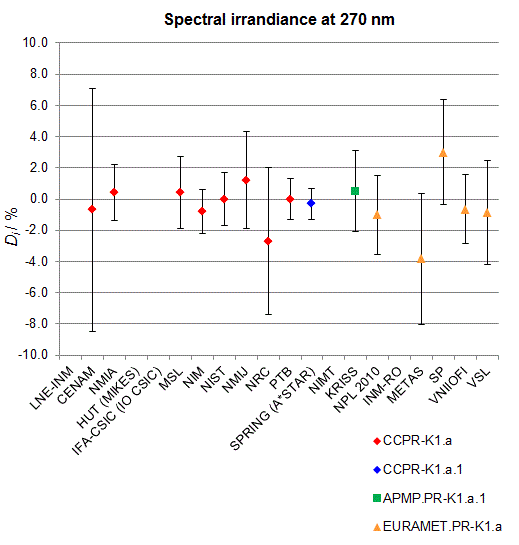
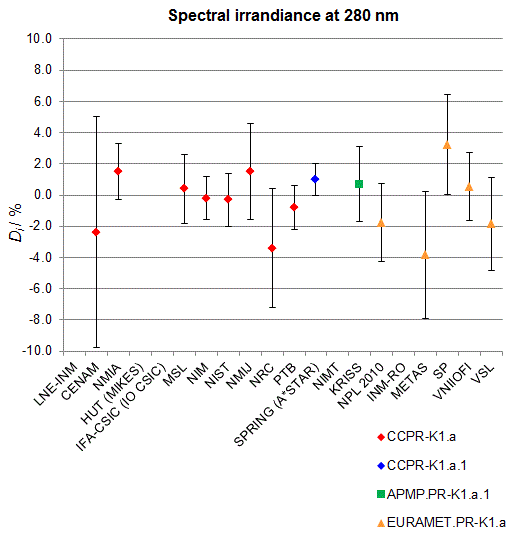
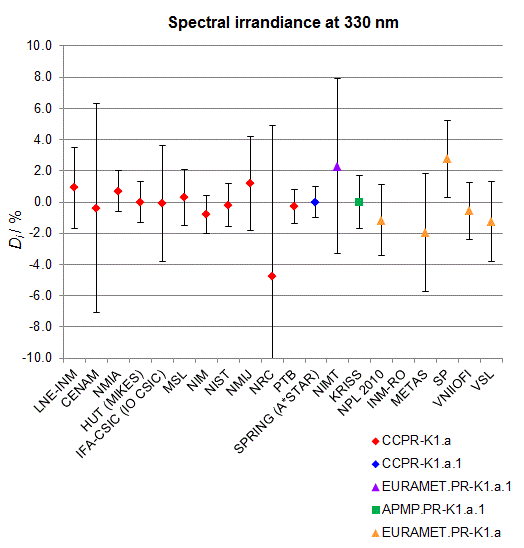
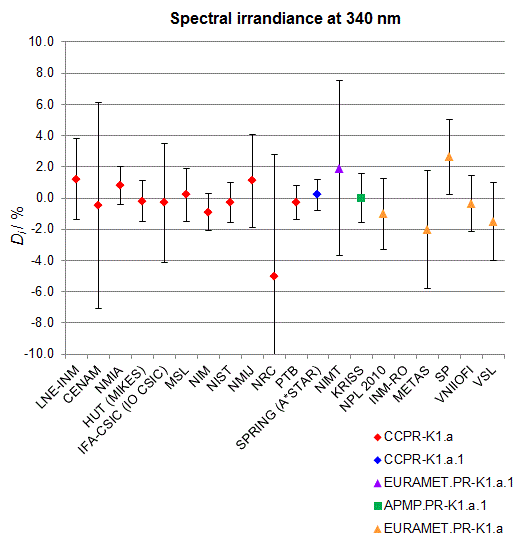
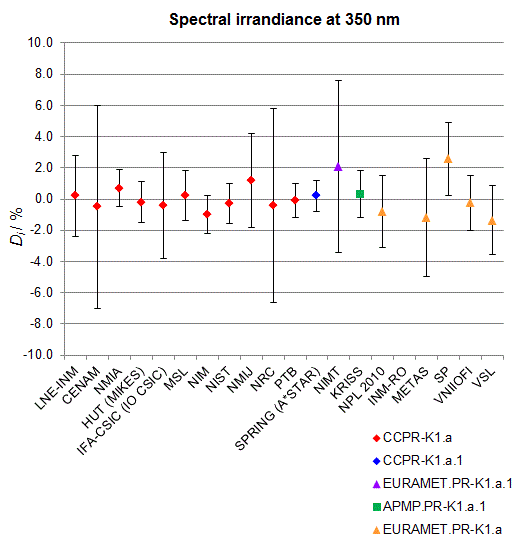
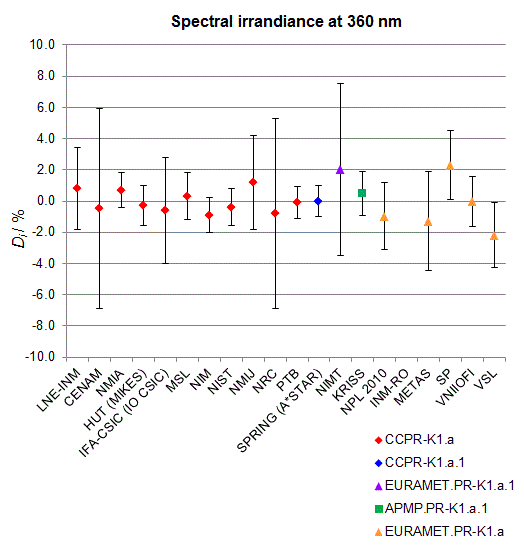
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 370 nm to 750 nm
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 800 nm to 1700 nm
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 1800 nm to 2500 nm
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
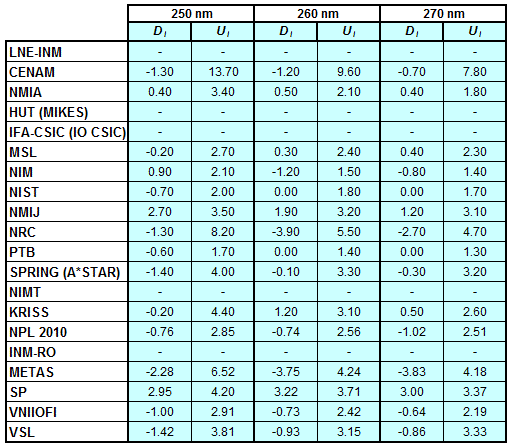
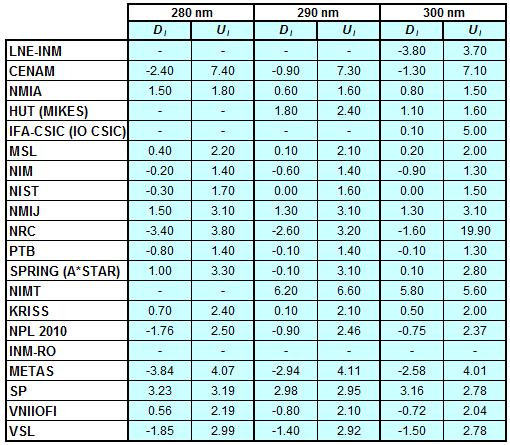
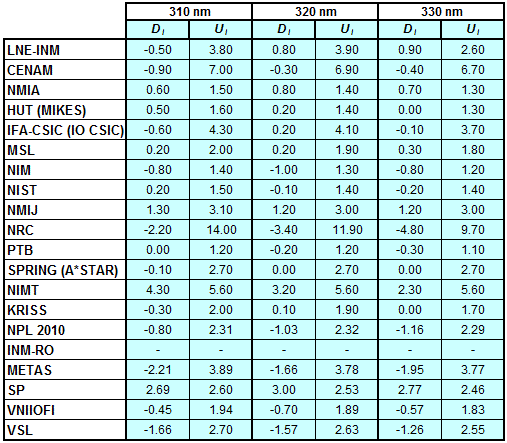
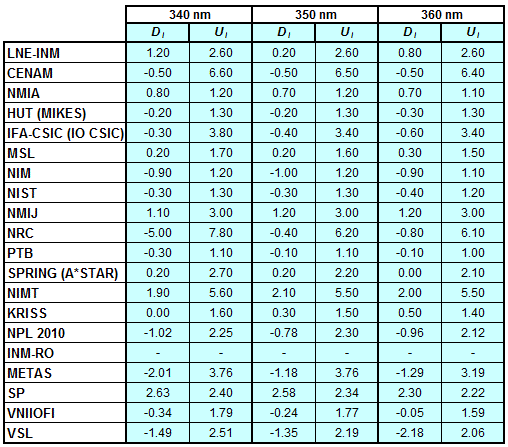
Degrees of Equivalence for spectral irradiance
in the interval from 250 nm to 360 nm
A*STAR (former SPRING) Singapore participated in CCPR-K1.a.1
NIMT participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
KRISS participated in APMP.PR-K1.a.1
NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and VSL participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (.PDF file).
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Degrees of Equivalence for spectral irradiance
in the interval from 370 nm to 750 nm
A*STAR (former SPRING) Singapore participated in CCPR-K1.a.1
NIMT participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
KRISS participated in APMP.PR-K1.a.1
NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and VSL participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (.PDF file).
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Degrees of Equivalence for spectral irradiance
in the interval from 800 nm to 1700 nm
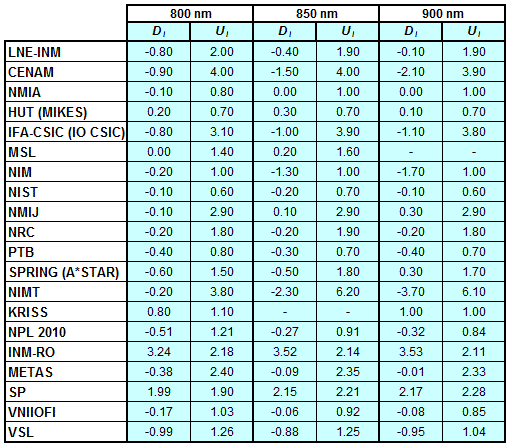
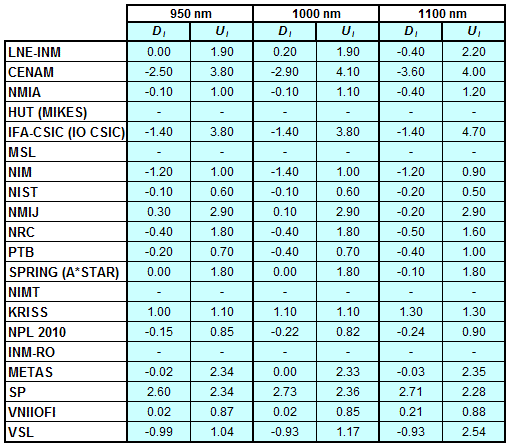
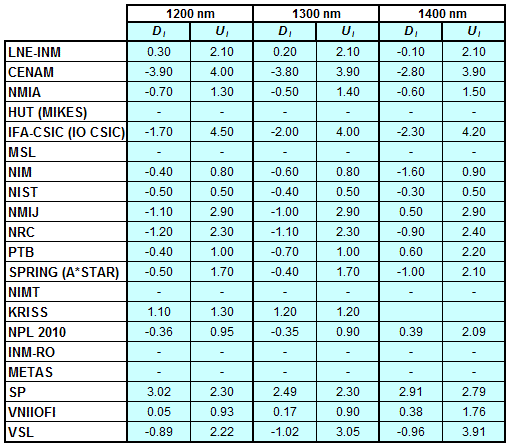
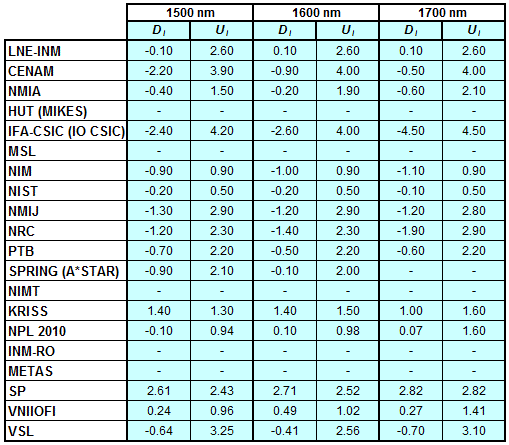
A*STAR (former SPRING) Singapore participated in CCPR-K1.a.1
NIMT participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
KRISS participated in APMP.PR-K1.a.1
NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and VSL participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (.PDF file).
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Degrees of Equivalence for spectral irradiance
in the interval from 1800 nm to 2500 nm
A*STAR (former SPRING) Singapore participated in CCPR-K1.a.1
NIMT participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
KRISS participated in APMP.PR-K1.a.1
NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and VSL participated in EURAMET.PR-K1.a
Results are presented under A4 printable format in Summary Results (.PDF file).
| Metrology area, Sub-field | Photometry and Radiometry, Properties of detectors and sources |
| Description | Spectral irradiance |
| Time of measurements | 2009 |
| Status | Approved for equivalence |
| Final Reports of the comparisons | |
| Measurand | Spectral irradiance |
| Parameters | Wavelength from 250 nm to 2500 nm |
| Transfer device | Detector Stabilized Lamps (DSL) |
| Comparison type | Key Comparison |
| Consultative Committee | CCPR (Consultative Committee for Photometry and Radiometry) |
| Conducted by | EURAMET (European Association of National Metrology Institutes) |
| Comments | Results published on 24 September 2015 CCPR-K1.a.1 results (from 250 nm to 1600 nm), EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 results (from 290 nm to 900 nm), APMP.PR-K1.a.1 and EURAMET.PR-K1.a results (from 250 nm to 2500 nm) are linked to those of CCPR-K1.a. Spectral irradiance from 250 nm to 2500 nm
|
| Pilot institute |
NPL
National Physical Laboratory United Kingdom |
| Contact person | T. Goodman +44 (0) 20 8943 6863 |
| Pilot laboratory | |
|---|---|
| NPL |
National Physical Laboratory, United Kingdom, EURAMET |
| INM |
National Institute of Metrology, Romania, EURAMET |
| METAS |
Federal Institute of Metrology, Switzerland, EURAMET |
| PTB |
Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Germany, EURAMET |
| SP |
Technical Research Institute of Sweden from 2017 Research Institutes of Sweden AB, Sweden, EURAMET |
| VNIIOFI |
All-Russian Scientific Institute for Optical and Physical Measurements, Rosstandart, Russian Federation, COOMET |
| VSL |
VSL, Netherlands, EURAMET |
This page proposes print-out on A4 paper (portrait) of the comparison details (best printed out using a black and white printer).
Please, select items to be printed out, then click on "OK" :
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
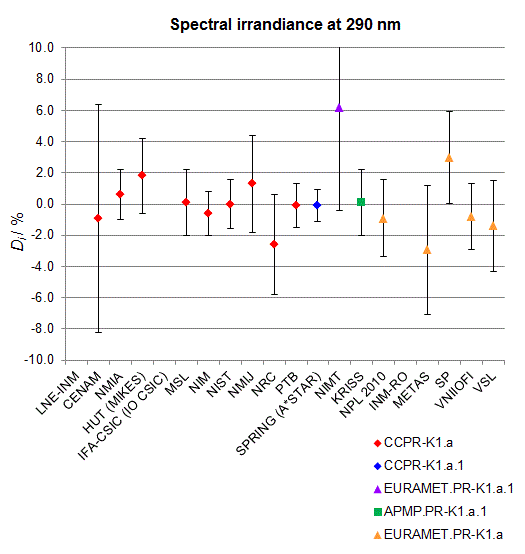
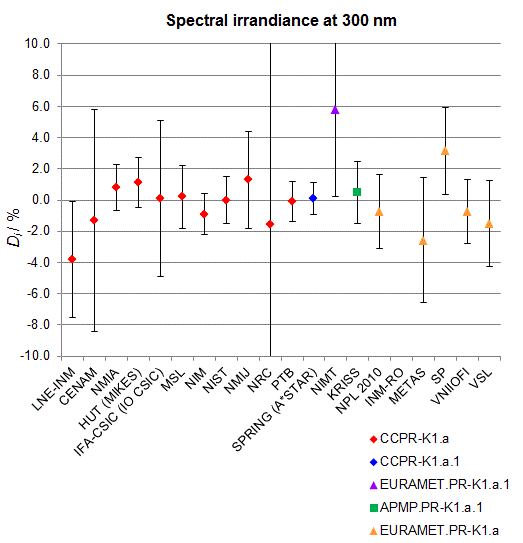
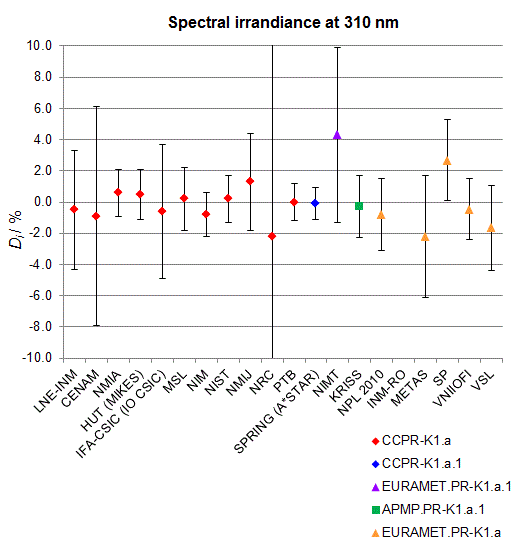
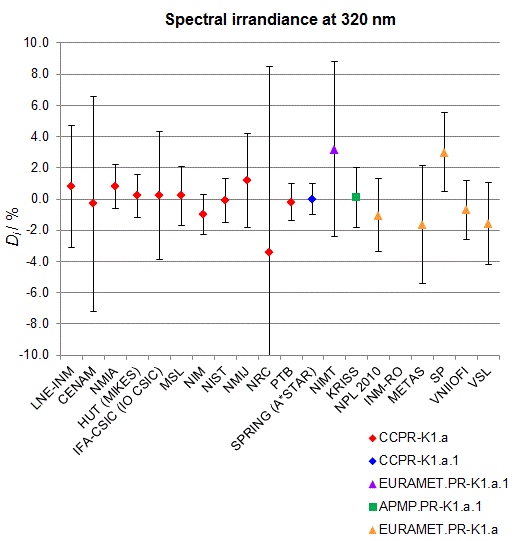
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 250 nm to 360 nm
n.b. All wavelengths within this interval are not covered by all listed comparisons (cf. Degrees of Equivalence)
|
This comparison was carried out independently at each wavelength. The key comparison reference value is calculated as the weighted geometric mean (with a cut-off) of the estimated systematic factors. It is stipulated to be unity by a special choice of the constraint equation. |
| The degree of equivalence of laboratory i with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di, the difference between the estimated systematic factor for that participant and the key comparison reference value, being unity, and Ui, its expanded uncertainty at a 95 % level of confidence (see section 17.6.2 of the CCPR-K1.a Final Report). Di and Ui are expressed in relative units. |
| CCPR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between NMIA and SPRING Singapore. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of SPRING Singapore relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the NMIA results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 9 of the CCPR-K1.a.1 Final Report (pages 20 to 24). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from SPRING Singapore. |
| APMP.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between KRISS and VNIIOFI. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of KRISS relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the VNIIOFI results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 6.2 and in Appendix C of the APMP.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from KRISS. |
|
EURAMET.PR-K1.a is a subsequent key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between the NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and the VSL. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with the results obtained by the EURAMET.PR-K1.a comparison. |
| EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between MIKES and NIMT. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of NIMT relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the MIKES (referred to as "HUT" at the time of the CCPR-K1.a key comparison) results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in the Appendix A of the EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report (page 12). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from NIMT. |
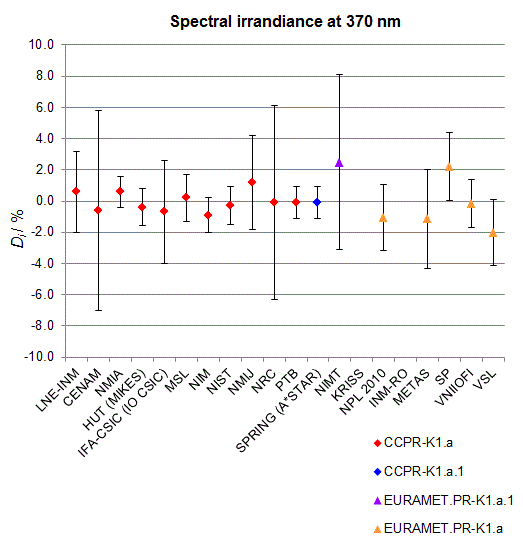
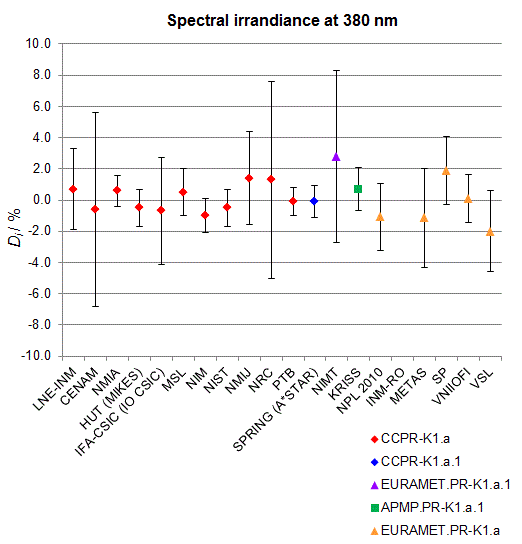
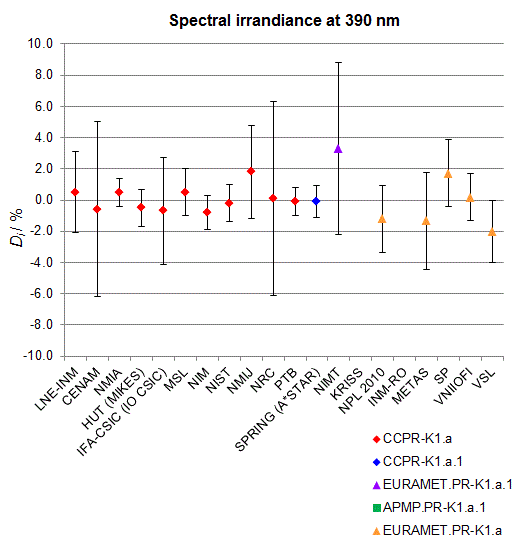
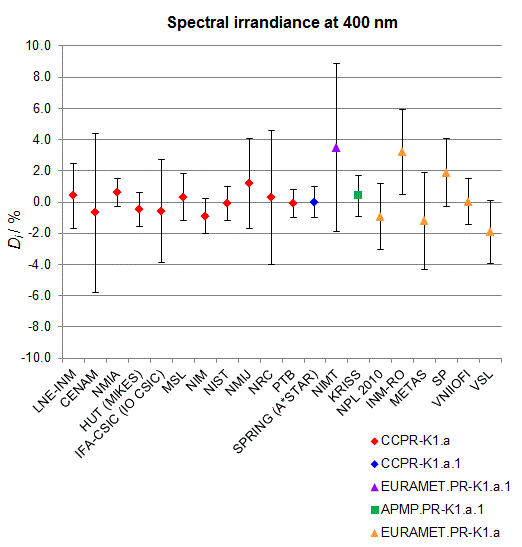
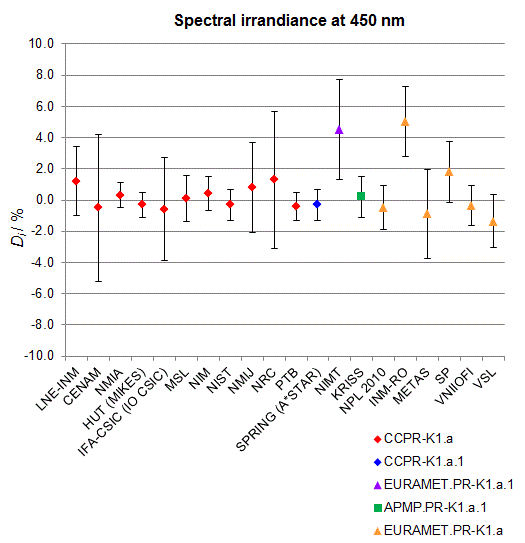
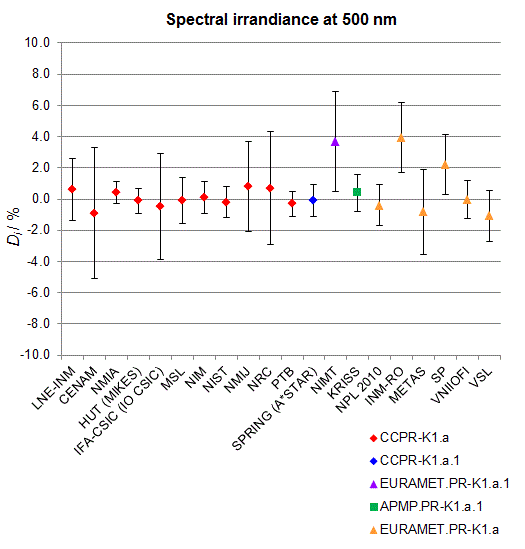
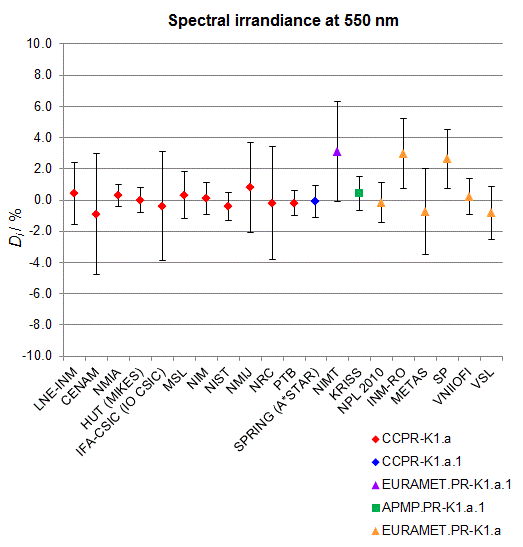
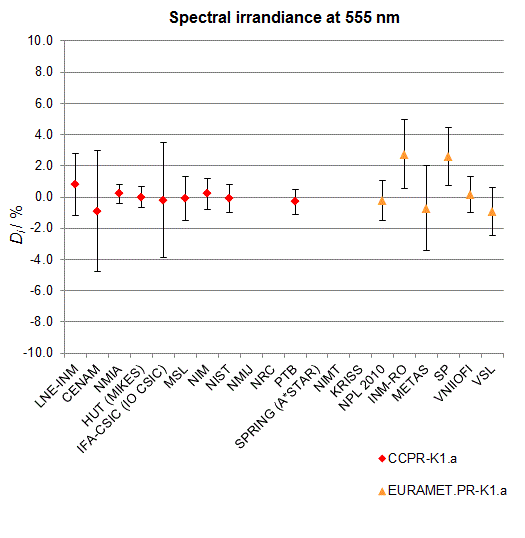
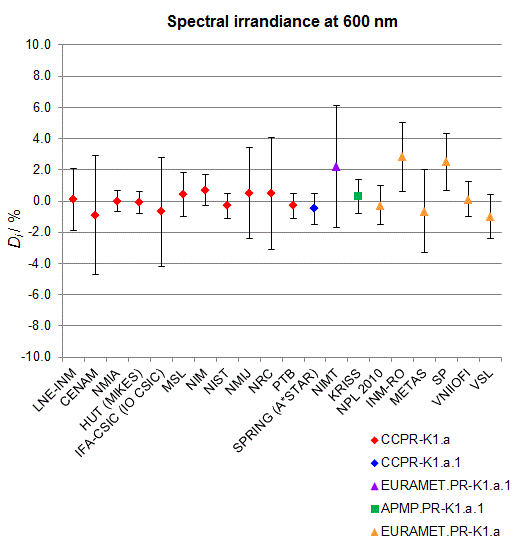
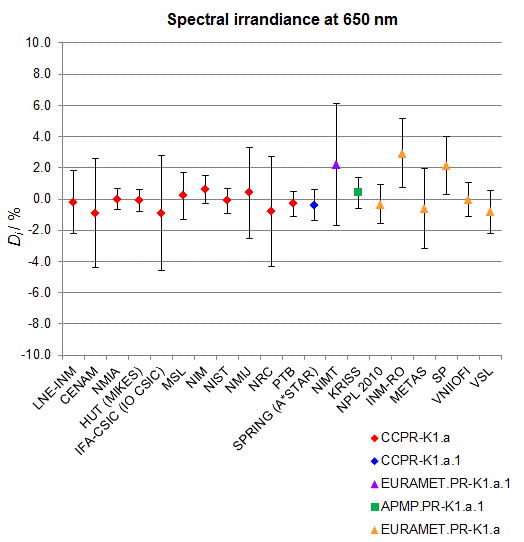
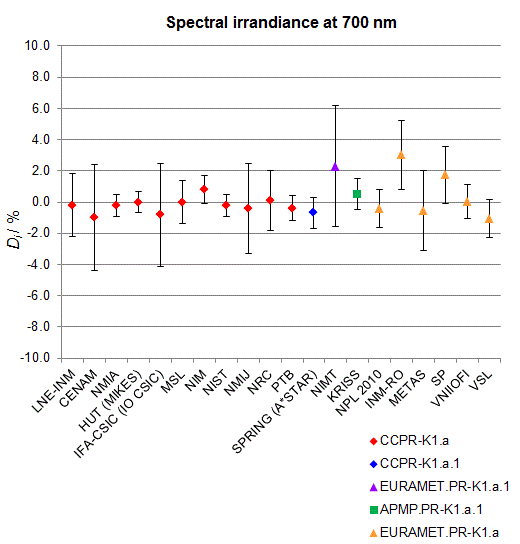
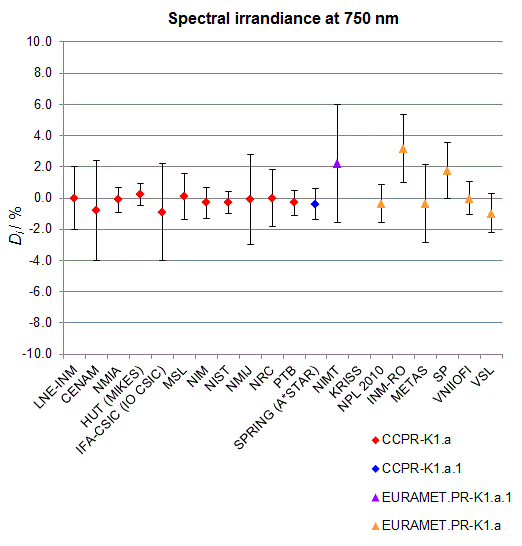
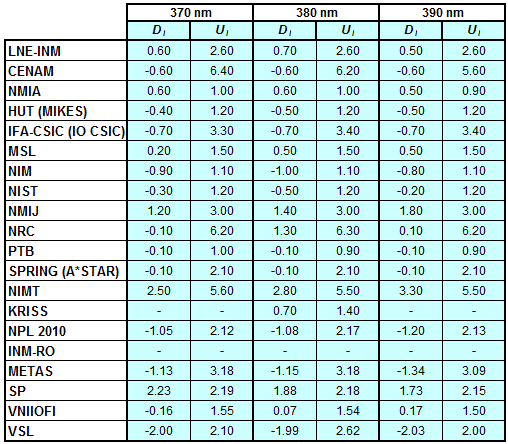
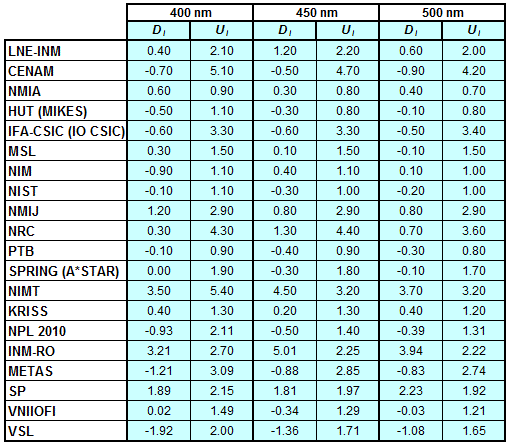
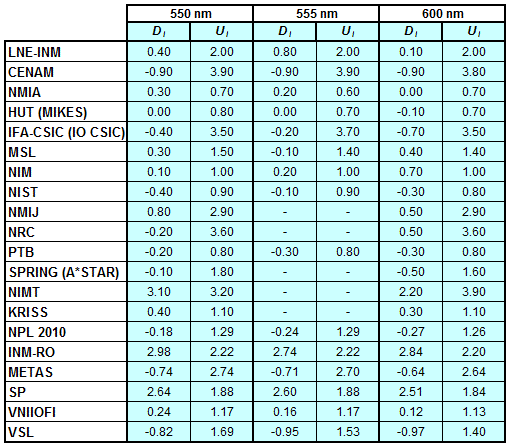
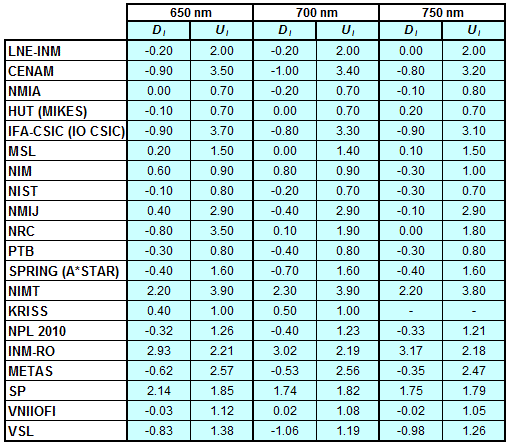
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 370 nm to 750 nm
n.b. All wavelengths within this interval are not covered by all listed comparisons (cf. Degrees of Equivalence)
|
This comparison was carried out independently at each wavelength. The key comparison reference value is calculated as the weighted geometric mean (with a cut-off) of the estimated systematic factors. It is stipulated to be unity by a special choice of the constraint equation. |
| The degree of equivalence of laboratory i with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di, the difference between the estimated systematic factor for that participant and the key comparison reference value, being unity, and Ui, its expanded uncertainty at a 95 % level of confidence (see section 17.6.2 of the CCPR-K1.a Final Report). Di and Ui are expressed in relative units. |
| CCPR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between NMIA and SPRING Singapore. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of SPRING Singapore relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the NMIA results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 9 of the CCPR-K1.a.1 Final Report (pages 20 to 24). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from SPRING Singapore. |
| APMP.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between KRISS and VNIIOFI. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of KRISS relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the VNIIOFI results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 6.2 and in Appendix C of the APMP.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from KRISS. |
|
EURAMET.PR-K1.a is a subsequent key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between the NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and the VSL. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with the results obtained by the EURAMET.PR-K1.a comparison. |
| EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between MIKES and NIMT. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of NIMT relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the MIKES (referred to as "HUT" at the time of the CCPR-K1.a key comparison) results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in the Appendix A of the EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report (page 12). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from NIMT. |
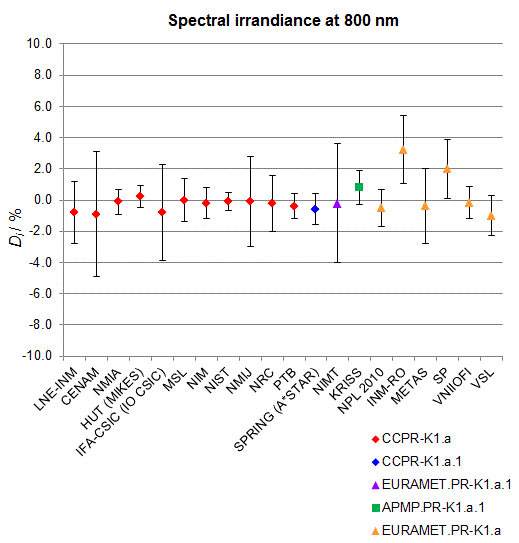
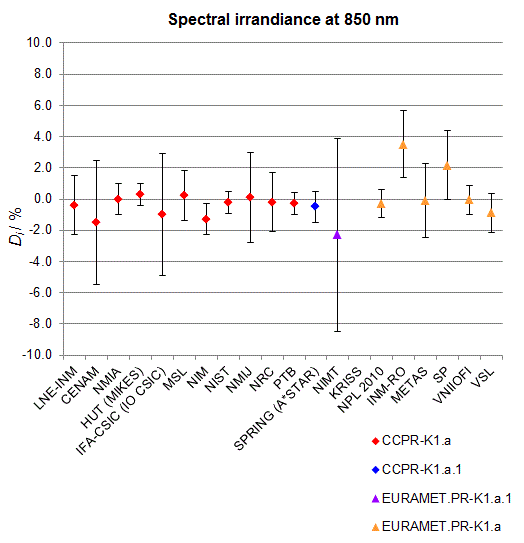
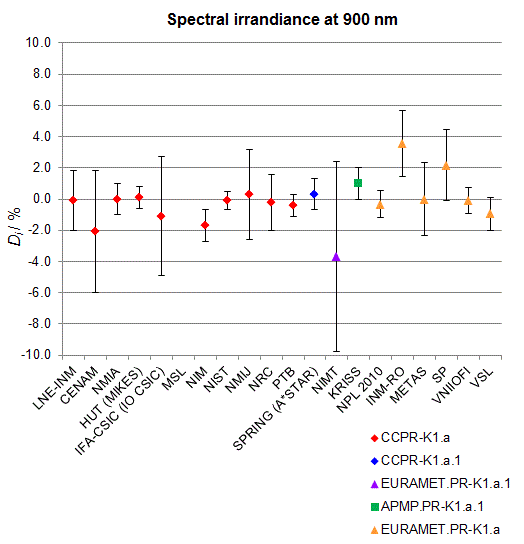
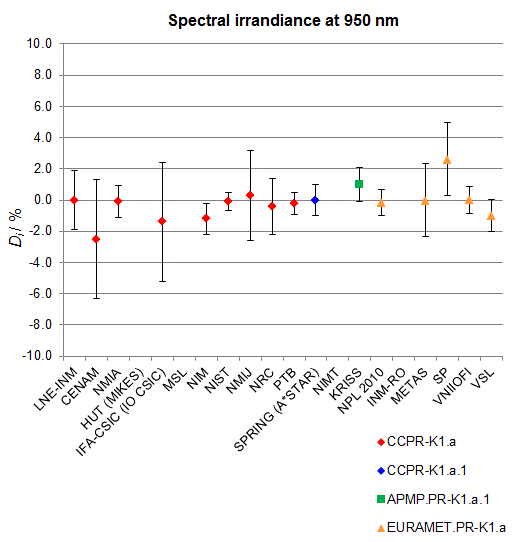
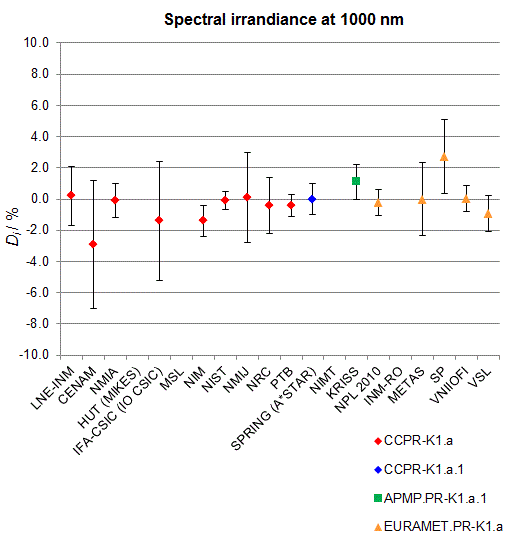
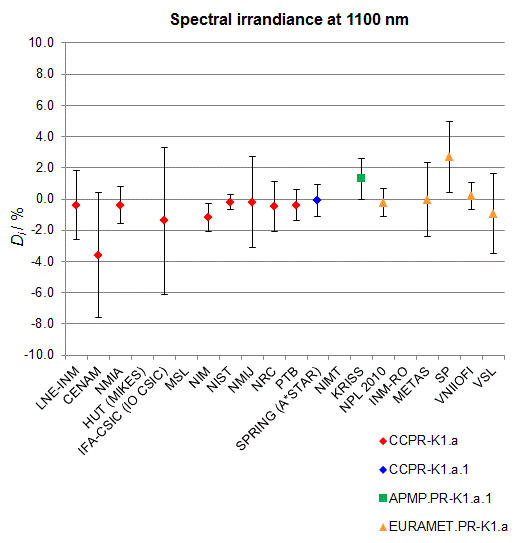
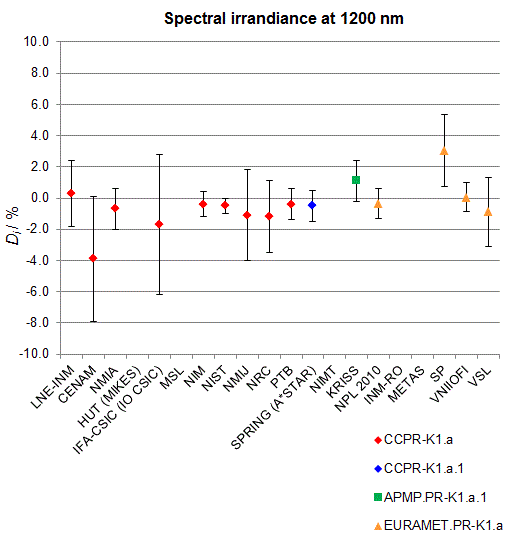
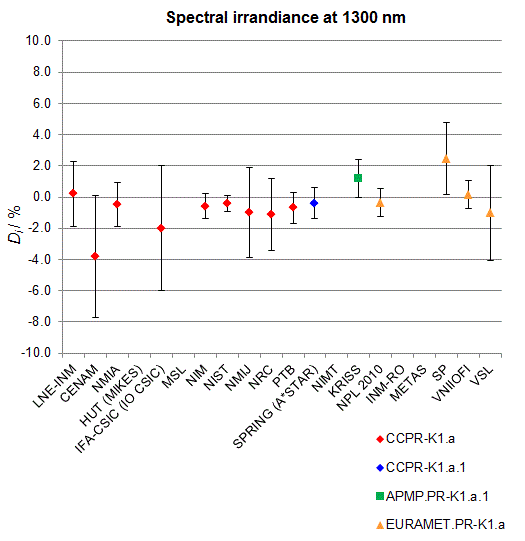
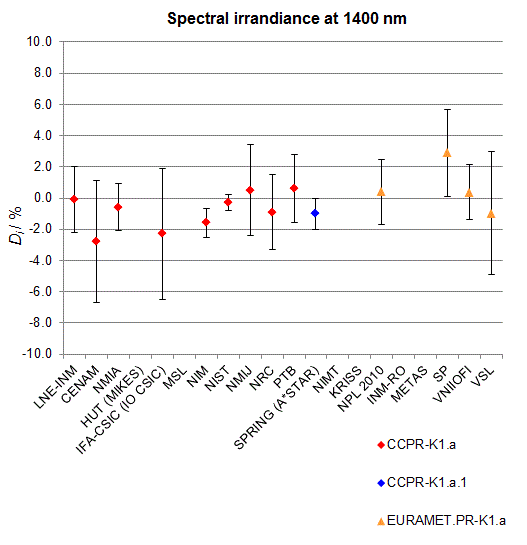
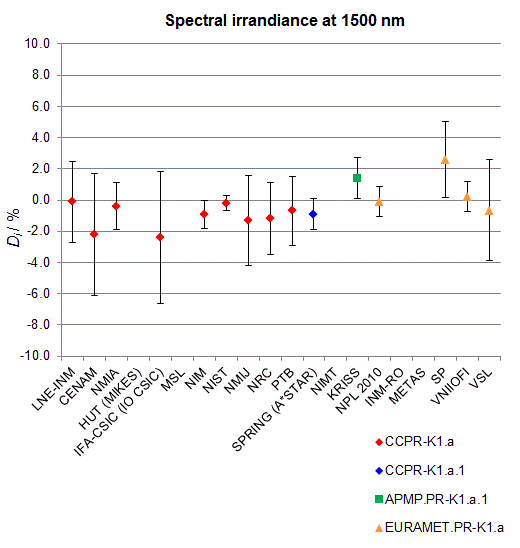
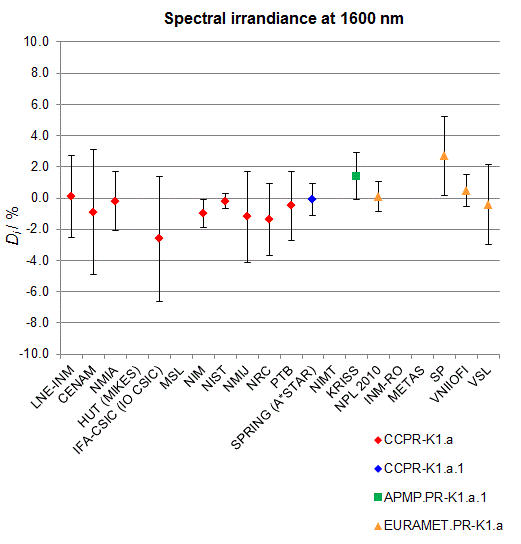
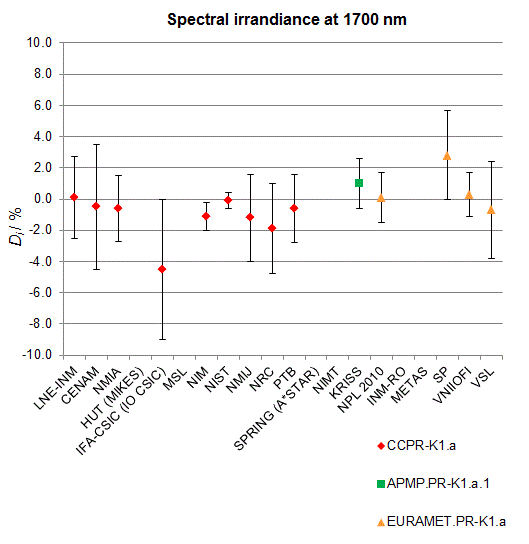
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 800 nm to 1700 nm
n.b. All wavelengths within this interval are not covered by all listed comparisons (cf. Degrees of Equivalence)
|
This comparison was carried out independently at each wavelength. The key comparison reference value is calculated as the weighted geometric mean (with a cut-off) of the estimated systematic factors. It is stipulated to be unity by a special choice of the constraint equation. |
| The degree of equivalence of laboratory i with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di, the difference between the estimated systematic factor for that participant and the key comparison reference value, being unity, and Ui, its expanded uncertainty at a 95 % level of confidence (see section 17.6.2 of the CCPR-K1.a Final Report). Di and Ui are expressed in relative units. |
| CCPR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between NMIA and SPRING Singapore. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of SPRING Singapore relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the NMIA results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 9 of the CCPR-K1.a.1 Final Report (pages 20 to 24). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from SPRING Singapore. |
| APMP.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between KRISS and VNIIOFI. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of KRISS relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the VNIIOFI results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 6.2 and in Appendix C of the APMP.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from KRISS. |
|
EURAMET.PR-K1.a is a subsequent key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between the NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and the VSL. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with the results obtained by the EURAMET.PR-K1.a comparison. |
| EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between MIKES and NIMT. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of NIMT relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the MIKES (referred to as "HUT" at the time of the CCPR-K1.a key comparison) results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in the Appendix A of the EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report (page 12). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from NIMT. |
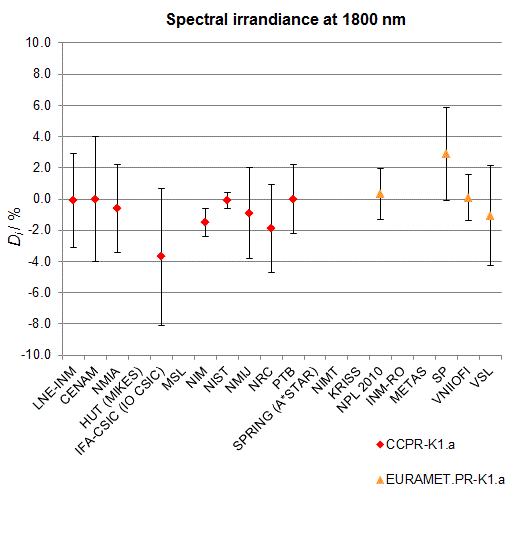
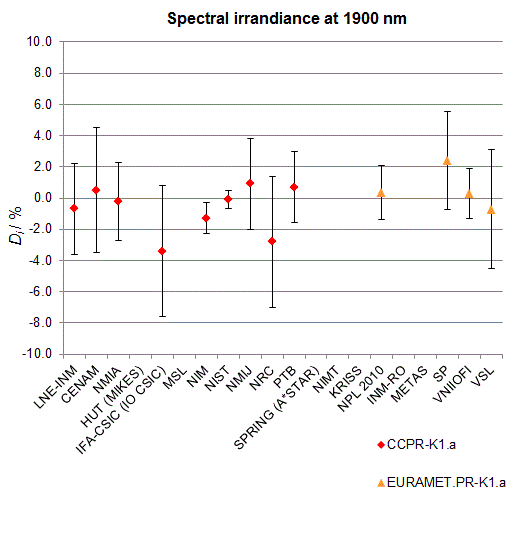
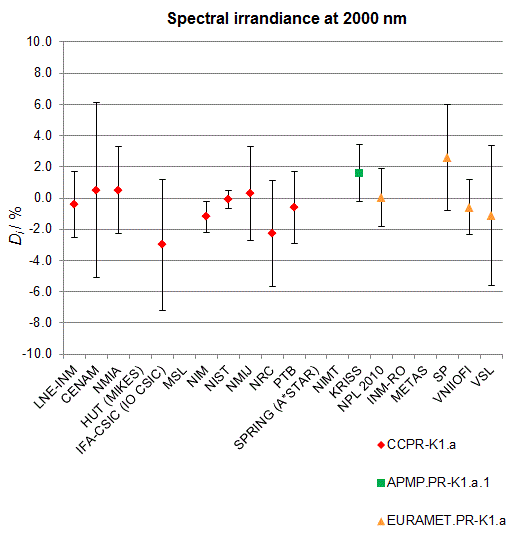
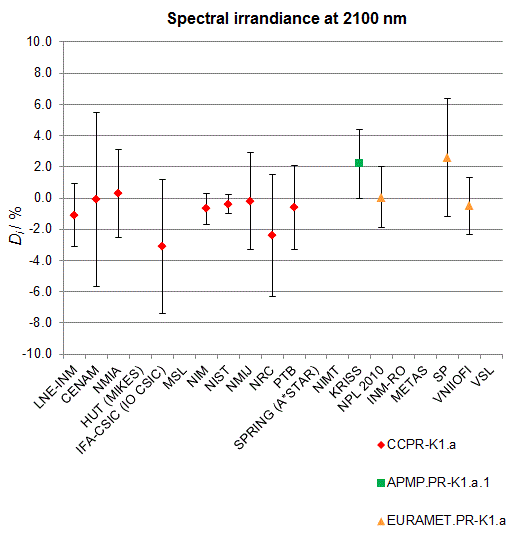
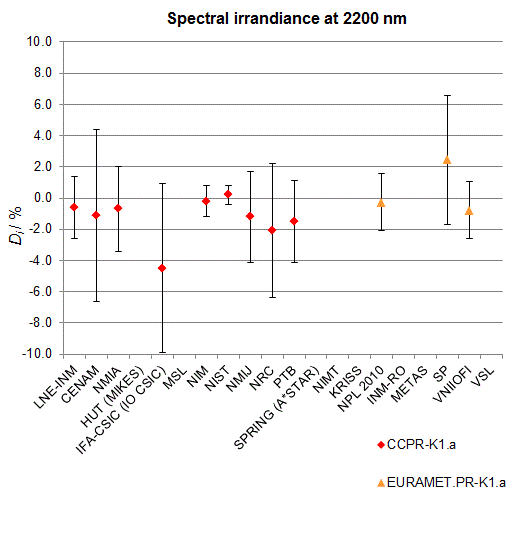
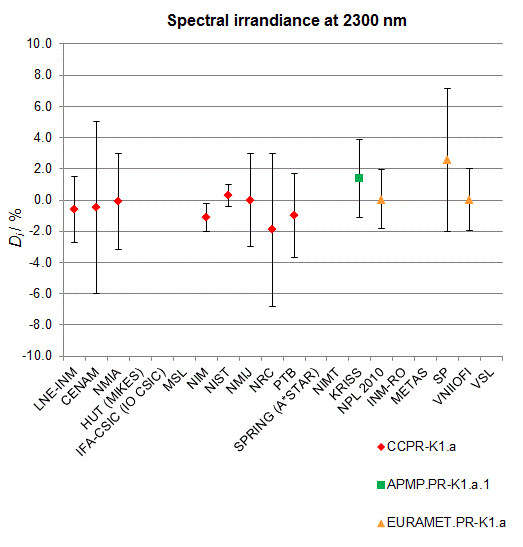
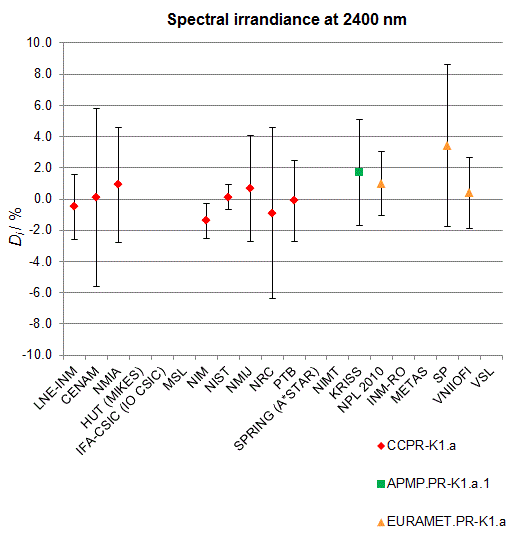
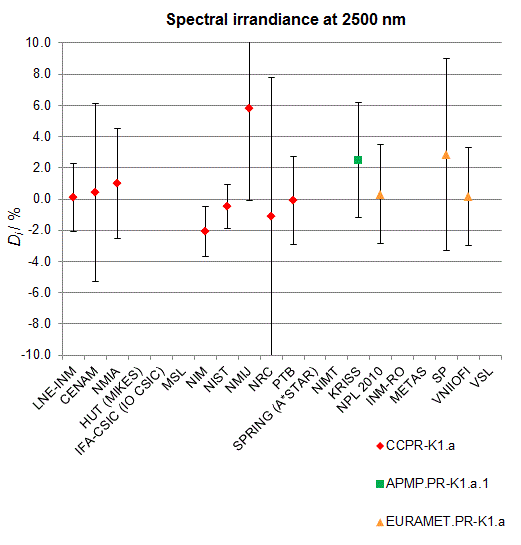
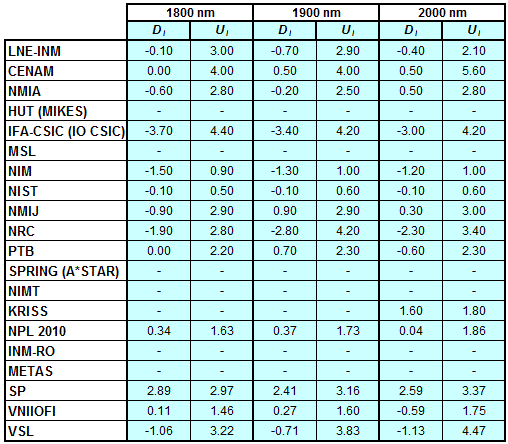
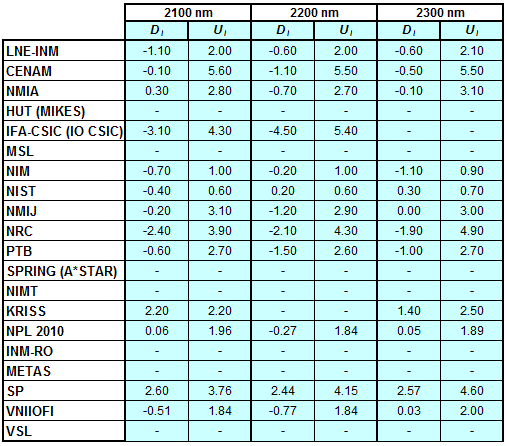
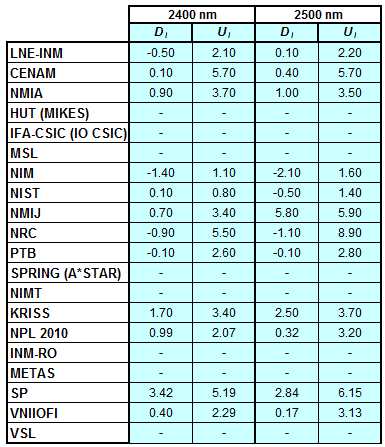
CCPR-K1.a, CCPR-K1.a.1, APMP.PR-K1.a.1, EURAMET.PR-K1.a and EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1
Spectral irradiance in the interval from 1800 nm to 2500 nm
n.b. All wavelengths within this interval are not covered by all listed comparisons (cf. Degrees of Equivalence)
|
This comparison was carried out independently at each wavelength. The key comparison reference value is calculated as the weighted geometric mean (with a cut-off) of the estimated systematic factors. It is stipulated to be unity by a special choice of the constraint equation. |
| The degree of equivalence of laboratory i with respect to the key comparison reference value is given by a pair of terms: Di, the difference between the estimated systematic factor for that participant and the key comparison reference value, being unity, and Ui, its expanded uncertainty at a 95 % level of confidence (see section 17.6.2 of the CCPR-K1.a Final Report). Di and Ui are expressed in relative units. |
| CCPR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between NMIA and SPRING Singapore. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of SPRING Singapore relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the NMIA results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 9 of the CCPR-K1.a.1 Final Report (pages 20 to 24). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from SPRING Singapore. |
| APMP.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between KRISS and VNIIOFI. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of KRISS relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the VNIIOFI results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in Section 6.2 and in Appendix C of the APMP.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from KRISS. |
|
EURAMET.PR-K1.a is a subsequent key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between the NPL, PTB, INM-RO, METAS, SP, VNIIOFI and the VSL. This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with the results obtained by the EURAMET.PR-K1.a comparison. |
| EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 is a subsequent bilateral key comparison to CCPR-K1.a, between MIKES and NIMT. At any one common wavelength to both comparisons, the degree of equivalence of NIMT relative to the CCPR-K1.a reference value is computed using the MIKES (referred to as "HUT" at the time of the CCPR-K1.a key comparison) results obtained in both comparisons, as explained in the Appendix A of the EURAMET.PR-K1.a.1 Final Report (page 12). This makes it possible to extend the CCPR-K1.a graphs of equivalence with one additional point from NIMT. |
Measurement data are available in the EURAMET.PR-K1.a Final Report.
Measurement data are available in the EURAMET.PR-K1.a Final Report.
Measurement data are available in the EURAMET.PR-K1.a Final Report.
Measurement data are available in the EURAMET.PR-K1.a Final Report.