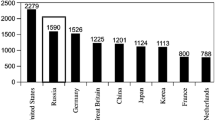
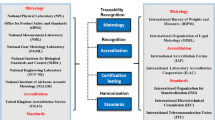
Abstract
The objective of this paper is to provide an economic perspective to those involved in public financing of the national metrology infrastructure. Whereas justifications for subsidising the national metrological activities are often historically biased, we raise the importance of economic considerations, which could be used during prioritisation. The expenditure in measurement and metrology infrastructure of European countries are compared to economic indicators for quality of life. Various proxies are used, such as measuring instruments sale (for measurement infrastructure) and data from the BIPM’s KCDB (as a proxy for national standards). As the EU Internal Market also holds for the provision of metrological services, the paper exposes possible trends regarding public financing to the sector.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For clarity, calibration refers to the operation that, under specified conditions, in a first step, establishes a relation between the quantity values with measurement uncertainties provided by measurement standards and corresponding indications with associated measurement uncertainties and, in a second step, uses this information to establish a relation for obtaining a measurement result from an indication [2].
References
Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology (JCGM/WG 2) (2008) International vocabulary of basic and general terms in metrology, 3rd edn. International Bureau of Weights and Measures—BIPM. http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/documents/jcgm/JCGM_200_2008.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
International Bureau of Weights and Measures—BIPM (2008). http://www.bipm.org. Accessed 5 May 2008
Howarth P, Redgrave F (2008) Metrology in short, 3rd edn. EURAMET. http://www.euramet.org/index.php?id=mis. Accessed 5 May 2008
Browns S (1999) Review of the rationale for an economic benefit of the UK national measurement system. Department of Trade and Industry—National Measurement System Policy Unit, UK. http://www.berr.gov.uk/files/file32855.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
Sangster RC (1976) Final summary report study of the national measurement system 1972-75. National Bureau of Standards, Boulder, Colorado, USA, 40 p (NBSIR 75-925)
The World Bank Statistical Manual (2008). http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/DATASTATISTICS/EXTDECSTAMAN/0,contentMDK:20882526~isCURL:Y~menuPK:2648252~pagePK:64168445~piPK:64168309~theSitePK:2077967,00.html. Accessed 5 May 2008
European Commission (1998) Setting the standard: 25 years of quality measurements. http://ec.europa.eu/research/growth/measure/pdf/measure_en.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Country scorings of the human development index (HDI) (2008). http://hdr.undp.org/en/statistics/. Accessed 5 May 2008
International Organisation for Standardisation—ISO. http://www.iso.org/iso/resources/conformity_assessment. Accessed 5 May 2008
Lord Sainsbury of Turville (2007) The Race to the top: a review of government’s science and innovation policies. HM Treasury, Norwich, UK. http://www.hm-treasury.gov.uk/sainsbury_review_index.htm. Accessed 5 May 2008
Cowen T (1992) Public goods and market failures: a critical examination. New Brunswick Transaction Publishers, New Jersey, USA (ISBN 156000570X, 9781560005704)
Pelkmans J (2006) Testing for subsidiarity, Bruges European economic policy briefings no 13, College of Europe. http://www.coleurop.be/template.asp?pagename=BEEP. Accessed 5 May 2008
Chambon M, Erard L (2005) Overview of the metrology landscape, implementing the metrology European research area—iMERA. http://www.euramet.org/. Accessed 5 May 2008
Swedish Government Offices (2007) Vissa metrologifrågor—Impact assessment of the Swedish metrology. Stockholm, Sweden. http://www.regeringen.se/sb/d/108/a/94170. Accessed 5 May 2008
Williams G (2002) The assessment of the economic role of measurements and testing in modern society. Final report, European Measurement Project, Pembroke College, University of Oxford
KCDB—Key comparison database (2008). http://kcdb.bipm.org/appendixC/. Accessed 5 May 2008
MacDonald M, De Cecco D, MacDonald I, Meriluoto L, Williams D (2002) Potential economic impact of the CIPM mutual recognition arrangement, KPMG. http://www.bipm.org/en/cipm-mra/economic.html. Accessed 5 May 2008
Easton B (1999) Metrology and the economy. Report for the Ministry of Consumer affairs, Wellington, New Zealand. http://www.consumeraffairs.govt.nz/policylawresearch/discussionpapers/metrologyeconomy.html. Accessed 5 May 2008
Statistical Office of the European Communities—EUROSTAT (2008). http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page?_pageid=1090,30070682,1090_33076576&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL. Accessed 5 May 2008
European Association of National Metrology Institutes—EURAMET (2008). http://www.euramet.org/. Accessed 5 May 2008
European Commission Proposal for a decision of the European Parliament and of the Council on the participation by the Community in a European Metrology Research and Development Programme undertaken by several Member States {SEC(2008)2948} {SEC(2008)2949} (2008). http://ec.europa.eu/research/index.cfm?pg=newsalert&lg=en&year=2008&na=na-011208. Accessed 5 May 2008
EMRP—European Metrology Research Program (2008). http://www.emrponline.eu. Accessed 5 May 2008
Consolidated versions of the Treaty on European Union and of the Treaty establishing the European Community (2006). Official Journal of the European Union C 321E of 29th December 2006. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/treaties/index.htm. Accessed 5 May 2008
Provisions from the Protocol (No 30) on the application of the principle of subsidiary and proportionality (attached to the Amsterdam Treaty) (2006). http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:C:2006:321E:0001:0331:EN:pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
Birch J (2003) Benefit of the legal metrology for the economy and society. International Organization of Legal Metrology—OIML. http://www.oiml.org/publications/E/birch/E002-e03.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
European Commission decision C (2006) 5477 of 22 November 2006 on State Aid implemented by France for the Laboratoire nationale de metrology et d’essais. Official Journal of the European Union from 5/4/2007. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2007:095:0025:0036:EN:PDF. Accessed 5 May 2008
BIPM (2007) Evolving needs for metrology in trade, industry and society and the role of the BIPM. International Bureau of Weights and Measures—BIPM. http://www1.bipm.org/utils/en/pdf/Kaarls2007.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
Swann GMP (1999) The economics of measurement. Report for the UK National Measurement System Review, Department for Business, Enterprise & Regulatory Reform, London, UK. http://www.berr.gov.uk/files/file9676.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poposki, N., Majcen, N. & Taylor, P. Assessing publically financed metrology expenditure against economic parameters. Accred Qual Assur 14, 359–368 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-009-0538-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-009-0538-3